Query parameters
Neo4j Browser supports querying based on parameters. It allows the Cypher query planner to re-use your queries instead of parse and build new execution plans.
Parameters can be used for:
-
literals and expressions
-
node and relationship IDs
Parameters cannot be used for the following constructs, as these form part of the query structure that is compiled into a query plan:
-
property keys
-
relationship types
-
labels
Parameters may consist of letters and numbers and any combination of these but cannot start with a number or a currency symbol.
|
For more details on the Cypher parameters, see Cypher Manual v.5 - Parameters. |
Set query parameters
You can set a parameter to be sent with your queries by using the :param command.
Using parameters rather than hard-coded values allows for the reuse of the query plan cache.
The :param name => 'Example' command defines a parameter named name, which will be sent along with your queries.
The right hand side of ⇒ is sent to the server and evaluated as Cypher with an implicit RETURN in front.
This gives better type safety since some types (especially numbers) in JavaScript are hard to match with Neo4j:s type system.
To see the list of all currently set query parameters and their values, use the :params command.
For more information on how to use the commands, see :help param and :help params.
|
If you are using a multi-database DBMS, parameters cannot be declared when using the |
:param x => 1:param x => 1.0:param x => "Example"-
Map
:param obj1 => ({props: {name: "Tom Hanks", born:1956}})The obj1 parameter$obj1 = {"props": {"name": "Tom Hanks", "born": 1956}}Maps like
{x: 1, y: 2}must be wrapped in parentheses({x: 1, y: 2}). -
List
:param obj2 => [1, 2, 3, 4]The obj2 parameter$obj2 = [1, 2, 3, 4]
:param name => 'Tom Hanks';MATCH (n:Person)
WHERE n.name = $name
RETURN n|
To run this example, in the Browser Settings drawer, check Enable multi statement query editor.
Note that the results are displayed in a different way when you run multiple statements.
In Neo4j Browser, the current state of multi-statement is to set up your environment with multiple statements so that you can execute queries and examine the results, one by one.
Alternatively, you can run the |
Cypher result
It is possible to save the result from a Cypher query to a parameter.
The syntax is:
:param <parameter_name> => { CYPHER STATEMENT }This example shows a result of one record returned.
:param result1 => { RETURN 1 AS foo }$result1 = [{foo: 1}]This example shows a result of three records returned.
:param result2 => { UNWIND [1, 2, 3] AS nbr RETURN nbr }$result2 = [{"nbr": 1}, {"nbr": 2}, {"nbr": 3}]}:param result3 => { MATCH (n) WHERE n.name = "Example" RETURN n }$result3 = [{"n": {"identity": 4, "labels": [], "properties": {"name": "Example"}}}]Destructuring
It is possible to pick individual values from your result using destructuring and set a specific parameter to a specific value.
The syntax is:
:param [{<returned_parameter>: <parameter_name>, ...}, ...] => { CYPHER STATEMENT }:param [{foo}] => { RETURN 1 AS foo }$foo = 1:param [{foo: bar}] => { RETURN 1 AS foo }$bar = 1:param [{foo1: bar1, foo2: bar2}] => { RETURN 1 AS foo1, 2 AS foo2 }$bar1 = 1
$bar2 = 2:param [{nbr: x}] => { UNWIND [2, 3, 1] AS nbr RETURN nbr ORDER BY nbr ASCENDING }$x = 1:param [nbr, nbr, nbr] => { UNWIND [2, 3, 1] AS nbr RETURN nbr ORDER BY nbr ASC }$nbr = 3:param [{nbr: x}, nbr, nbr] => { UNWIND [2, 3, 1] AS nbr RETURN nbr ORDER BY nbr ASC }$x = 1
$nbr = 3:param [{nbr: x}, {nbr: y}, {nbr: z}] => { UNWIND [2, 3, 1] AS nbr RETURN nbr ORDER BY nbr ASC }$x = 1
$y = 2
$z = 3:param [{n: example}] => { MATCH (n) WHERE n.name = "Example" RETURN n LIMIT 1}$example = {"identity": 4, "labels": [], "properties": {"name": "Example"}}}Clear parameters
You can clear all currently set parameters from Neo4j Browser by running:
:params {}Set several parameters
You can set several parameters with the :params command, this also clears all currently set parameters.
|
Integers are set to float with this style. |
:params {x: 1, y: 2.0, z: 'abc', d: null, e: true, f: false}$x = 1.0
$y = 2.0
$z = "abc"
$d = null
$e = true
$f = falseParameter assistance
If you run a query using parameters without first declaring them all, Browser returns a ParameterMissing error and lists the missing parameter(s).
You can click the provided template to populate the editor with the command for setting parameters and all you have to do is enter the value(s) for the missing parameter(s).
Since the result frame is reusable, once you have set your parameter(s), you can run the same Cypher query again without having to re-enter it.
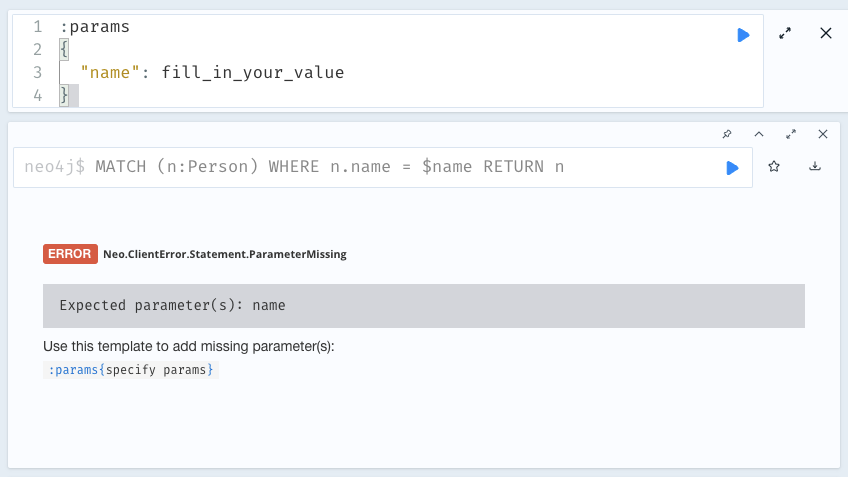
|
The command offered with parameter assistance is always |