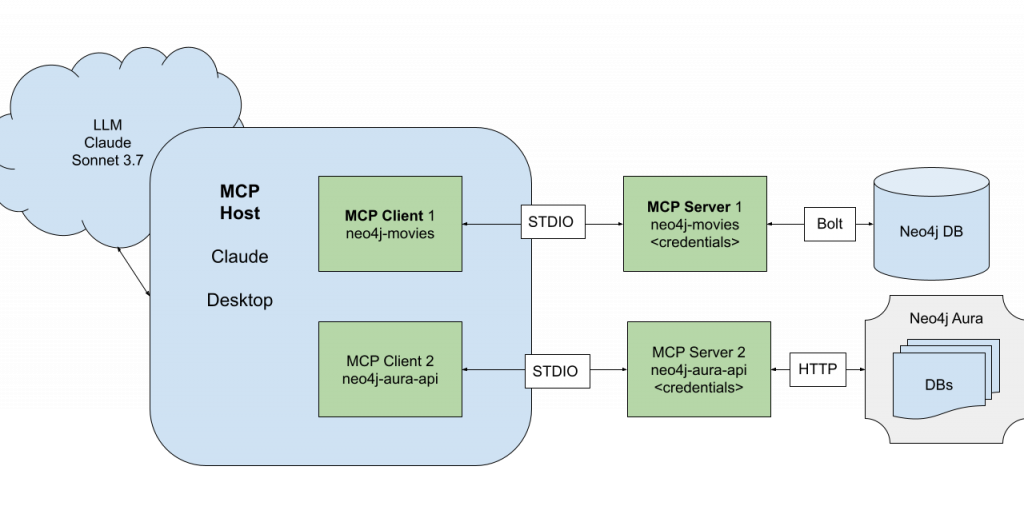
Neo4j + Cassandra: Transferring Data from a Column Store to a Property Graph

Senior Product Manager
5 min read

[Editor’s Note:] This Neo4j Lab has been deprecated. The code is available in our GitHub project, but is no longer actively maintained.
We’ve previously talked about the concept of polyglot persistence and why it can make sense to use multiple database technologies together.
Today, we will examine a possible use case for using Neo4j (a graph database) and Cassandra (a column store) together and take a brief look at the alpha version of a new tool to help make working with Cassandra and Neo4j a bit easier.
Data Model Translation: A Challenge of Polyglot Persistence

Figure 1: Converting a column store data model into a property graph. Converting from one data model to another is often the first step of implementing polyglot persistence.
Polyglot persistence is all about taking advantage of the strengths of multiple database technologies to enhance your application. However, this comes at the expense of the added complexity of working with multiple databases.
In order to take advantage of polyglot persistence, often the first task is to convert from one data model to another. For example, converting data from a document data model to a property graph model.
Our goal is to make this process more simple for the developer. For this reason, we have been working on a prototype Neo4j-Cassandra data import tool.
Neo4j + Cassandra: A Possible Use Case
Before looking at this tool, let’s examine why we would want to use Cassandra and Neo4j together.
Previously, we looked at using MongoDB and Neo4j together in the context of a product catalog use case. In that example, we leveraged Neo4j for generating personalized recommendations while using MongoDB’s strengths to search, filter and populate the view for our product catalog.
What are the strengths of each database that we would want to leverage? Because of Cassandra’s masterless clustering model and reliance on eventual consistency, one of its strengths is the ability to handle a very high write throughput. For this reason, Cassandra is often used to store high volume data such as event logs, which don’t require ACID guarantees like what is available with Neo4j.
However, depending on how we want to analyze these event logs, we might run into trouble.
As Cassandra does not have a rich query language, it is advised to make the columns and column families optimized for reading the data. This can result in data duplication as you end up creating new tables with the same data, but optimized for different queries.
What if we want to explore relationships in our data, perhaps for a fraud detection use case?
We know that Neo4j is very good at handling relationships, so it might make sense to bring some of our event log data into Neo4j to run some fraud detection Cypher queries.
Fraud detection using event log data is just one possible use case that might make sense. Do you have a polyglot Neo4j + Cassandra use case in mind? If so we’d love to hear from you about it!
The Neo4j-Cassandra Data Import Tool – Alpha Version

Figure 2: The Neo4j Cassandra Data Import tool enables data export from Cassandra, translation to a property graph and inserting into Neo4j.
To help developers take advantage of polyglot persistence with Neo4j and Cassandra, we’ve put some effort into developing a command-line tool to enable transferring data from Cassandra to Neo4j. Special thanks to Hanneli Tavante who helped develop this project with the use of her Cassandra expertise!
Note that this is just an alpha prototype version that demonstrates some of the issues and a possible approach. Community feedback and contributions are much appreciated.
An Overview of the Tool
The Neo4j-Cassandra data import tool works by inspecting the Cassandra schema and allowing the user to define how the data should be mapped from Cassandra’s column-oriented data model into a Neo4j property graph:
Step 1: Inspect Cassandra Schema and Config Data Mapping
The tool will inspect the Cassandra schema and generate a file with placeholders for specifying the configuration mapping.
This initial version of the tool provides limited options for translation, the most notable limitation is that every table will be translated into a node in the graph model. See the documentation for more information.
CREATE TABLE playlist.artists_by_first_letter:
first_letter text: {}
artist text: {}
PRIMARY KEY (first_letter {}, artist {})
CREATE TABLE playlist.track_by_id:
track_id uuid PRIMARY KEY: {}
artist text: {}
genre text: {}
music_file text: {}
track text: {}
track_length_in_seconds int: {}
NEO4J CREDENTIALS (url {}, user {}, password {})
Figure 3: The tool inspects the Cassandra schema of a specified keyspace. The user must then configure the mappings of the data model to specify how the property graph is created.
Step 2: Import Data to Neo4j
Once the mapping has been specified by the user, the tool provides a mechanism to generate LOAD CSV Cypher queries to automatically import the data set from Cassandra to Neo4j.
This is accomplished by writing to CSV files as an intermediate step, then using Neo4j’s LOAD CSV Cypher import tooling to import the data. The Cypher queries are executed using Neo4j’s Python bindings (py2neo) based on the credentials specified as part of the data mapping.
An initial version of the tool is available now available on Github here. Note that the tool is rather limited in scope at this point and has only been tested with an example dataset, as explained in the documentation.
Looking Forward
This was a brief look at the challenges of polyglot data modelling and a new tool that makes that process a bit easier (hopefully) when working with transferring data from Cassandra to Neo4j.
By no means is this tool a complete and scalable solution for syncing data from Cassandra to Neo4j. This tool is simply the first step toward providing a solution for implementing polyglot persistence using Cassandra and Neo4j.
Our goal is to provide a simple example and a use case of what might make sense. If you are interested in providing feedback, please email me or raise an issue on the GitHub project. We’d love to hear from those using Cassandra and Neo4j together. What is your use case? What would help facilitate the polyglot Neo4j and Cassandra experience? We’re also very open to accepting Pull Requests on the GitHub project for those interested in contributing.
If you’re interested, you can read the individual steps for running the tool on our developer pages.
Looking for more advanced lessons on Neo4j? Register for our free Neo4j in Production class and take your graph database skills up another notch.