But how do companies today use graph databases to solve tough problems? In this blog series, we’ll cover the top 10 use cases for graph technology and for each we include a real-world example. This blog series continues with a look at using graph technology with knowledge graphs.
The previous blog in our ten-part series analyzed how graph technology can aid in network and IT operations management. In this seventh blog in our ten-part series, we turn our attention to how graph technology is the foundation of effective master data management. Master data is often fragmented and in need of adaptable foundational technology to function best. Graph technology allows companies to connect master data and evolve with the needs of the business, as exemplified in a case study of Airbnb.
Use Case #7: Master Data Management
Master data is the lifeblood of your enterprise, including data such as:
- Users
- Customers
- Products
- Accounts
- Partners
- Sites
- Business units
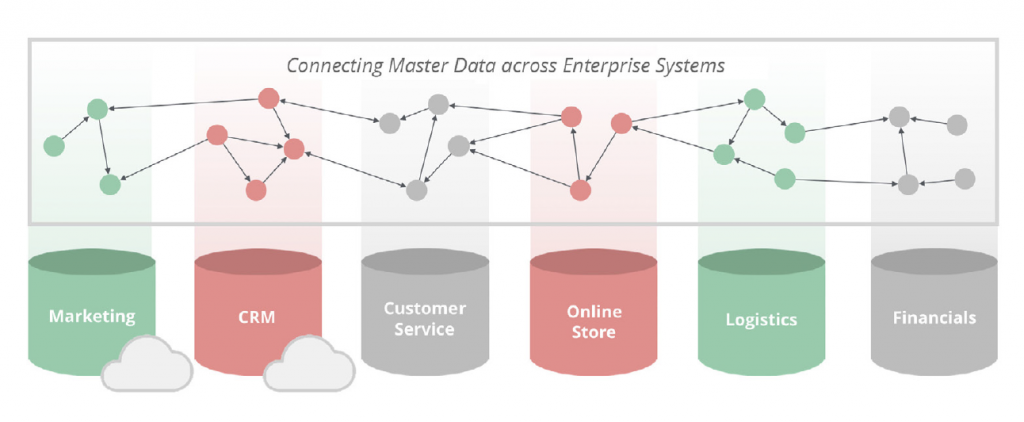
Many business applications use master data. It’s often held in many different places, with lots of overlap and redundancy, in different formats, and with varying degrees of quality. Master data management (MDM) is the practice of identifying, cleaning, storing, and – most importantly – governing this data.
MDM best practices vary, from merging all master data into a single location to managing data assets for easy access from a single service or application.
In both cases (or any hybrid solution), enterprise data architects need a data model that provides for ad hoc, variable and exceptional structures as business requirements change. This rapidly evolving model fits best with a graph database.
Why Use Graph Technology for Master Data Management?
Because master data is highly connected and shared, poorly built MDM systems cost business agility in a way that ripples throughout your enterprise. Most legacy MDM systems rely on a relational database that isn’t optimized for traversing relationships or rapid responsiveness.
These data connections and relationships in your master datasets are essential to competitive advantage as business analytics evolve. The good news is that graph databases are ideal for modeling, storing and querying the hierarchies, metadata and connections in your master data.
With graph databases, your master data is much easier to model and costs fewer resources (modelers, architects, DBAs and developers) than building a relational solution. In addition, you don’t have to migrate all of your master data into a single location. Graph relationships easily connect your siloed data between CRM systems, inventory systems, accounting and point-of-sale systems to provide a consistent vision of your enterprise data.
Example: Airbnb
In a large, complex organization such as Airbnb, an ever-growing landscape of internal and external data resources – especially when scattered across various platforms – eventually becomes unmanageable and restrictive.
Airbnb Software Engineer John Bodley recognized that Airbnb’s data was prohibitively siloed, inaccessible or lacked proper context. He also noticed that employees were relying on tribal knowledge for answers to questions, which stifled productivity.
“We often run an employee survey,” he said, “and we consistently scored really poorly around the question: ‘The information I need to do my job is easy to find.'” Bodley’s team knew they needed to democratize data so any employee, regardless of data-literacy level, was empowered to find resources, fully confident the results were relevant and reliable.
His team set off developing the Dataportal, a self-service, integrated data-space that presents a contextual, holistic view of Airbnb data for employees to navigate their data landscape whenever they need access or answers for their daily working needs.
Bodley and his team quickly realized their entire data ecosystem was best represented as a graph. That led them to the Neo4j graph database, which offered the fastest way to search through millions of data connections per second. Neo4j also integrated well with Airbnb’s preferred programming languages while also allowing them to enrich search rankings by taking advantage of the graph topology.
With Neo4j, Airbnb was able to tie together their entire data ecosystem and make it searchable, relevant and trustworthy. Instead of far-flung staffers relying on tribal knowledge, the Dataportal is Airbnb’s one-stop resource for finding relevant data, especially for employee- and team-centric information critical to daily performance.
Conclusion
The best data-driven business decisions aren’t based on stale information silos. Instead, you need real-time master data with information about data relationships.
Graph databases are built from the ground up to support these relationships. With more efficient modeling and querying, organizing your master data in a graph yields relevant answers faster and more flexibly than ever before.
Our next blog will tackle how graph technology can be the backbone organizations more effectively meeting their data lineage demands.
Download My Free Copy