LangChain Library Adds Full Support for Neo4j Vector Index

Graph ML and GenAI Research, Neo4j
6 min read

When you give large language models (LLMs) the power to search beyond their own fixed knowledge and pull in information from the wider world, you have more options for LLM-powered applications. This technique of retrieving data from external sources is called retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
RAG applications can be built using LangChain, the leading framework for developing LLM-powered applications. LangChain simplifies the development process by integrating most LLM providers and databases in a unified interface. The Neo4j vector index in the LangChain library allows developers to easily implement advanced vector indexing for efficient storage and retrieval of vector embeddings.
In this blog post, we’ll demonstrate how to use LangChain and Neo4j vector index to build a simple RAG application that can effectively answer questions based on information from a Wikipedia article. We’ll walk you through the following steps:
As always, the code is available on GitHub.
Neo4j Environment Setup
You need to set up Neo4j 5.11 or later to follow along with the examples in this blog post. The easiest way is to start a free instance on Neo4j Aura, which offers cloud instances of the Neo4j database. You can also set up a local Neo4j database by downloading the Neo4j Desktop application and creating a local database instance.
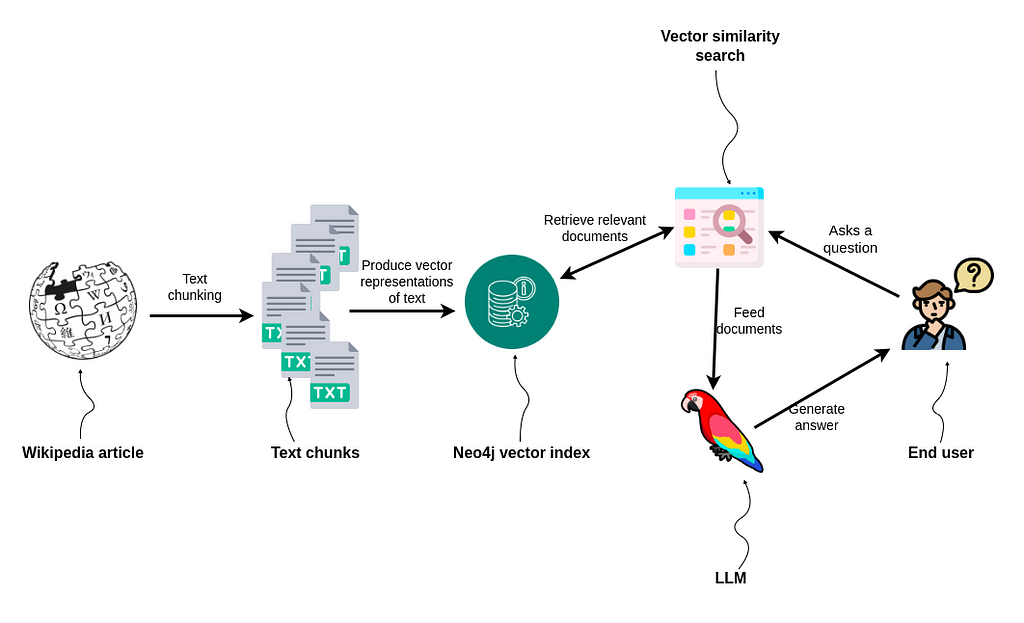
1. Reading and Chunking a Wikipedia Article
We’ll begin by reading and chunking a Wikipedia article. The process is pretty simple, as LangChain has integrated the Wikipedia document loader and the text chunking modules:
from langchain.document_loaders import WikipediaLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter
# Read the wikipedia article
raw_documents = WikipediaLoader(query="Leonhard Euler").load()
# Define chunking strategy
text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=20
)
# Chunk the document
documents = text_splitter.split_documents(raw_documents)
# Remove summary from metadata
for d in documents:
del d.metadata['summary']
Neo4j is a graph database, so it’s only fitting that we’re using the Wikipedia article on the father of graph theory, Leonhard Euler.
Next, we use the tiktoken text chunking module, which uses a tokenizer made by OpenAI, to split the article into chunks with 1000 tokens. You can learn more about text chunking strategies in this article.
LangChain’s WikipediaLoader adds a summary to each chunk by default. I thought the added summaries were a bit redundant. If you used a vector similarity search to retrieve the top three results, the summary would be repeated three times. Therefore, I decided to remove it from the dataset.
2. Storing and Indexing the Text With Neo4j
LangChain makes it easy to import the documents into Neo4j and index them using the newly added vector index. We’ve created a user-friendly interface that doesn’t require any prior knowledge of Neo4j or graphs. We also gave advanced users customization options, which we’ll discuss in the following blog post.
Neo4j vector index is wrapped as a LangChain vector store. Therefore, it follows the syntax used to interact with other vector databases.
from langchain.vectorstores import Neo4jVector
from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
# Neo4j Aura credentials
url="neo4j+s://.databases.neo4j.io"
username="neo4j"
password="<insert password>"
# Instantiate Neo4j vector from documents
neo4j_vector = Neo4jVector.from_documents(
documents,
OpenAIEmbeddings(),
url=url,
username=username,
password=password
)
The from_documents method connects to a Neo4j database, imports and embeds the documents, and creates a vector index. The data will be represented as the `Chunk` nodes by default. As mentioned, you can customize how to store the data and which data to return.
If you already have an existing vector index with populated data, you can use the from_existing_index method.
3. Performing Vector Similarity Search
We’ll begin with a simple vector similarity search to verify that everything works as intended:
query = "Where did Euler grow up?" results = neo4j_vector.similarity_search(query, k=1) print(results[0].page_content)
Results

The LangChain module used the specified embedding function (OpenAI in this example) to embed the question and then find the most similar documents by comparing the cosine similarity between the user question and indexed documents.
Neo4j Vector index also supports the Euclidean similarity metric along with the cosine similarity.
4. Implementing Question-Answering Workflow
LangChain supports question-answering workflows using only a line or two of code. For example, we can use the following code to create a question-answering workflow that generates answers based on the context given and provides the source documents:
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQAWithSourcesChain
chain = RetrievalQAWithSourcesChain.from_chain_type(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0),
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=neo4j_vector.as_retriever()
)
query = "What is Euler credited for popularizing?"
chain(
{"question": query},
return_only_outputs=True,
)
Results

As you see, the LLM constructed an accurate answer based on the Wikipedia article and returned the sources it used — and we only needed one line of code.
While testing the code, I noticed that the sources were not always returned. The problem here is not Neo4j vector implementation but rather GPT-3.5-turbo. Sometimes, it doesn’t listen to instructions to return the source documents. But if you use GPT-4, the problem goes away.
Lastly, to replicate the ChatGPT interface, you can add a memory module. It provides the LLM with dialogue history so we can ask follow-up questions. We only need two lines of code:
from langchain.chains import ConversationalRetrievalChain
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history", return_messages=True)
qa = ConversationalRetrievalChain.from_llm(
ChatOpenAI(temperature=0), neo4j_vector.as_retriever(), memory=memory)
Let’s now test it out.
print(qa({"question": "What is Euler credited for popularizing?"})["answer"])
Results

And now a follow-up question.
print(qa({"question": "Where did he grow up?"})["answer"])
Results

Building RAG Applications Made Simple
The LangChain integration streamlines the process of integrating Neo4j’s vector index into your existing or new RAG applications, which means you don’t have to dwell on the details.
LangChain already supports generating Cypher statements and using the generated Cypher to retrieve context; you can use it today to retrieve both structured and unstructured information.
Learning Resources
To learn more about building smarter LLM applications with knowledge graphs, check out the other posts in this blog series.