What Is Supply Chain Management? A Guide to Optimizing SCM

Senior Staff Writer
15 min read

Modern supply chains span vast networks, and today’s leaders prioritize resilience, agility, and sustainability. They also recognize that in an increasingly competitive environment, a data-driven approach to supply chain management (SCM) is essential. In fact, by 2027, 65% of supply chain professionals expect big data and advanced analytics to reshape supply chains.
Supply chain planning continues to be a data challenge, and businesses must figure out how to gather, analyze, and act on real-time insights. Traditional manual processes for managing supplier data often create inefficiencies and result in delays and slower time to market. By contrast, modern solutions including graph technology provide real-time visibility and enable supply chain optimization.
For instance, a global organization using graph technology to manage logistics and supply chain management swiftly resolved fleet disruptions caused by traffic, wildfires, and equipment failures. By integrating data across operations, they addressed issues and rerouted drivers in real time.
In this article, we’ll explore logistics and supply chain management, strategies for supply chain optimization, and how graph technology helps drive supply chain agility, resilience, and transparency.
What is Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management (SCM) involves coordinating and overseeing every stage involved in the production and delivery of goods, from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product to the customer. Effective end-to-end supply chain planning ensures that the right products are available at the right time, in the right quantity, and at the right cost, optimizing both efficiency and customer satisfaction.
At its core, logistics and supply chain management involves several key components that must work seamlessly together:
- Sourcing: Identifying and selecting suppliers who provide the necessary raw materials or components at the best possible cost and quality.
- Procurement: Negotiating contracts and purchasing goods or services that are essential for production.
- Production: Managing the manufacturing process to ensure efficiency, quality control, and timely output.
- Inventory management: Maintaining optimal stock levels to meet demand without overproducing, which ties up capital, or underproducing, which risks delays and stockouts.
- Warehousing: Storing goods safely and efficiently until they are ready for distribution.
- Transportation: Ensuring timely delivery of goods to various distribution points or directly to customers through reliable shipping and logistics solutions.
How Does Supply Chain Management Work?
The supply chain management process involves a series of interconnected steps that guide the flow of goods from raw materials to the final product reaching the customer. Each step must work in sync with the others to ensure efficiency, minimize costs, and meet customer demands. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how SCM works:
1. Planning: Demand forecasting and supply planning
The first stage in SCM is planning, where companies use demand forecasting to predict future customer needs and create supply plans to meet those demands. Accurate forecasting is crucial to avoid overproduction, stockouts, or wasted resources. Using real-time data analysis and advanced analytics, companies have the supply chain visibility to make informed decisions about production volumes, inventory levels, and procurement schedules.
2. Sourcing: Selecting suppliers and negotiating contracts
In the sourcing phase, companies select the suppliers that will provide the necessary raw materials or components. Sourcing involves evaluating suppliers on factors such as price, quality, reliability, and sustainability. Once selected, companies negotiate contracts to secure favorable terms. This stage is crucial for ensuring a consistent supply of materials and minimizing risks related to supplier disruptions.
3. Manufacturing: Production scheduling and quality control
Once materials are sourced, the manufacturing phase begins. This involves production scheduling, which ensures that manufacturing activities are aligned with demand forecasts. Quality control is also essential at this stage to ensure that the final product meets the required standards. Efficient manufacturing processes minimize waste and optimize production capacity, contributing to overall supply chain efficiency.
4. Delivery and logistics: Warehousing, transportation, and distribution
In this phase, the focus shifts to the storage and movement of goods. Warehouse management involves storing products until they are ready to be distributed to customers or retailers. Transportation ensures that goods move efficiently through the supply chain, whether through ground, air, or sea. Logistics and supply chain management must be tightly coordinated to minimize delays and optimize delivery routes, ensuring that products reach their final destinations on time.
5. Returns management: Handling product returns and recycling
An often overlooked component of SCM is returns management. This includes handling product returns, exchanges, and recycling. Effective returns management helps maintain customer satisfaction and allows companies to recover value through product refurbishment or recycling. As sustainability becomes a growing concern, companies increasingly focus on handling product returns in an environmentally friendly manner.
These steps must be fully integrated to support effective supply chain management. Breakdowns at any point can disrupt the entire chain, leading to increased costs, delays, and reduced customer satisfaction.
Incorporating supply chain management software and technologies like graph databases can also help companies visualize the relationships between these processes, uncover hidden bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions that improve overall supply chain optimization. By understanding and optimizing these interdependencies, businesses can build more agile, resilient, and cost-effective supply chains.
Why Supply Chains Can’t Be Modernized on Legacy Systems
Relying on legacy supply chain solutions often hinders a business’s ability to optimize its supply chain. Legacy systems lack the necessary functionality because they are typically rigid, slow to adapt, and unable to handle the vast amounts of real-time data required for today’s complex supply chains. These outdated infrastructures lack the flexibility needed to integrate new technologies like advanced analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and real-time tracking.
Without real-time visibility and automation, supply chain management is inefficient, which causes delays and limits scalability. However, modern cloud-based systems and graph databases offer the agility, scalability, and data-driven insights necessary for supply chain optimization.
Challenges in Supply Chain Management and How to Overcome Them
Modern supply chain management faces a range of challenges that significantly impact business performance, from supply chain disruptions and lack of visibility to managing fluctuating consumer demands. These obstacles become more pronounced as supply chains grow more complex and are geographically dispersed, often spanning multiple continents and involving diverse networks of factories, warehouses, and transportation routes.
To address these challenges, many companies rely on supply chain intelligence—a data-driven approach that provides real-time insights and analytics across the supply chain. By leveraging technologies such as graph databases and AI-powered analytics, businesses can better understand the interconnectivity between different supply chain components and make informed decisions to mitigate disruptions, control costs, and improve responsiveness.
For instance, companies can:
- Improve end-to-end visibility by tracking goods in transit in real time, providing a clear understanding of inventory levels and potential bottlenecks.
- Enhance forecasting by analyzing complex supply chain relationships and using predictive models to anticipate disruptions and their ripple effects.
- Enable real-time decision-making, allowing businesses to quickly respond to unexpected changes in supply or demand by harnessing vast amounts of disparate supply chain data.
- Control costs by using holistic cost-control analytics, such as root-cause analysis, to identify inefficiencies and make strategic adjustments across the entire network.
- Meet sustainability goals by tracking social and environmental impact, such as carbon footprints, and ensuring compliance with sustainability and ethical sourcing standards.
Key Benefits of Effective SCM
Implementing an efficient and well-integrated supply chain management (SCM) system offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance a company’s performance and competitiveness. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Improved efficiency and reduced costs
By optimizing workflows and ensuring better coordination between suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics partners, companies can lower operational costs. Automating processes and using real-time data analysis also minimizes errors, reduces delays, and ensures that resources are allocated efficiently. Ultimately, companies that prioritize supply chain efficiency see substantial savings in areas like transportation, warehousing, and inventory management.
2. Enhanced customer satisfaction through timely deliveries
A well-managed supply chain ensures that products reach customers on time, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty. By utilizing advanced forecasting and real-time tracking, companies can better anticipate demand, prevent stockouts, and ensure timely deliveries.
3. Better inventory management and reduced excess stock
By leveraging data-driven tools and supply chain intelligence, companies can maintain optimal stock levels, avoiding both overstocking and understocking scenarios. This leads to reduced excess inventory costs, more efficient use of storage space, and less capital tied up in unsold goods. At the same time, improved inventory management helps ensure that products are available when customers need them, enhancing both profitability and service quality.
4. Increased agility and adaptability to market changes
One of the biggest advantages of a robust SCM system is its ability to make companies more agile and responsive to unexpected changes in the market. Whether it’s a sudden shift in consumer demand, a new competitor, or a supply chain disruption, companies with a flexible and well-coordinated supply chain can quickly adapt. Using real-time data and advanced analytics, businesses can adjust production schedules, reallocate resources, and reroute shipments as needed, ensuring minimal disruption to operations and faster responses to evolving market conditions.
What is Supply Chain Optimization?
Supply chain optimization is the process of improving the efficiency and effectiveness of supply chain operations to maximize performance while minimizing costs. It involves fine-tuning each aspect of the supply chain, from procurement and production to logistics and delivery, ensuring that all components work together seamlessly to meet customer demand at the lowest possible cost.
Effective supply chain optimization relies on several key techniques:
1. Demand Planning
By using historical data, market analysis, and predictive analytics, companies can align their production schedules and inventory levels with expected demand, preventing stockouts or excess inventory. Accurate demand planning helps companies avoid costly disruptions and ensures they are prepared to meet customer needs promptly.
2. Inventory Optimization
Inventory optimization ensures that a company maintains the right amount of stock at all times—neither too much nor too little. The use of real-time data and predictive analytics allows companies to adjust inventory levels dynamically, keeping the supply chain lean and reducing excess stock.
3. Route Optimization
Companies can reduce transportation costs, lower fuel consumption, and speed up delivery times by optimizing routes.
A critical element of supply chain optimization is the emphasis on continuous improvement. As market conditions, customer preferences, and technological capabilities evolve, companies must continually refine their supply chain processes to stay competitive. Data-driven decision-making enables continuous improvement. By leveraging real-time data and advanced analytics, companies can gain deep insights into their supply chain performance and make informed decisions that drive long-term success. This data-driven approach helps companies to proactively address potential issues, respond quickly to disruptions, and identify opportunities for further optimization.
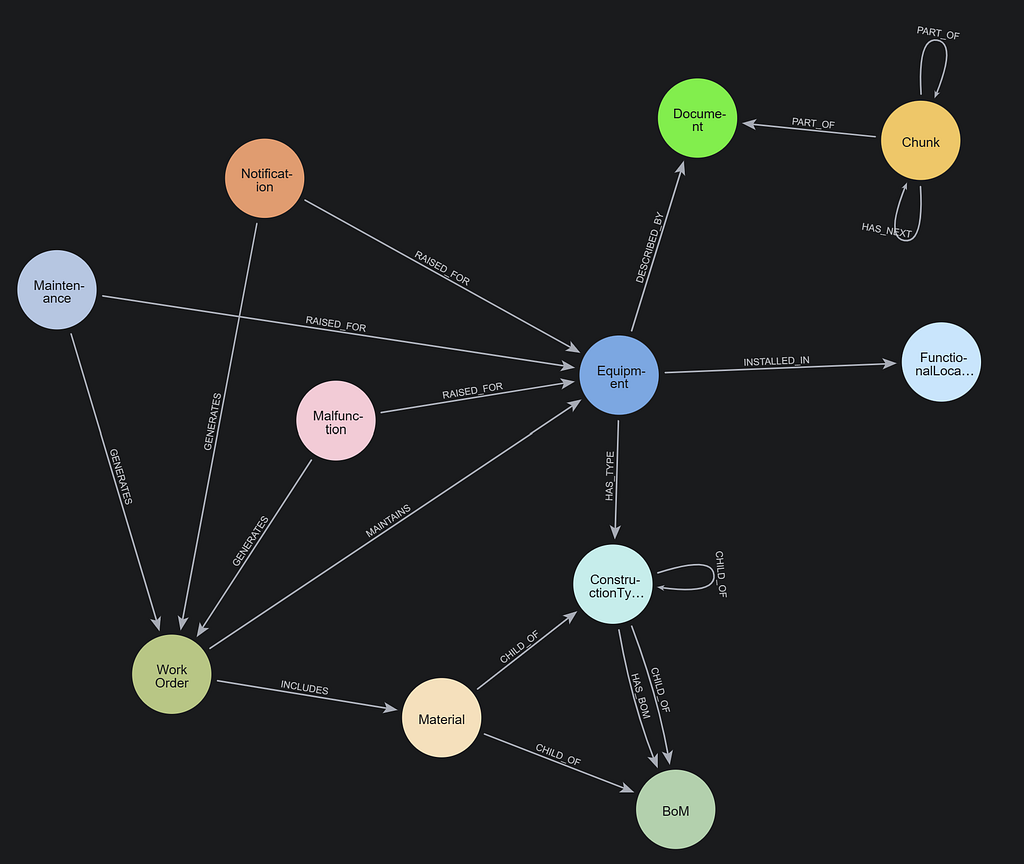
How Graph Technology Optimizes Supply Chain Management
Graph technology is a powerful solution for modern supply chain management, providing companies with the ability to model and analyze the complex, interconnected relationships that exist within a global supply chain. By visualizing these intricate networks and uncovering hidden patterns, graph databases help businesses make more informed, data-driven decisions that optimize supply chain efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance responsiveness to disruptions.
Graph databases can help:
1. Visualize complex supply chain networks
One of the greatest strengths of graph databases lies in their ability to map out the entire supply chain, from suppliers and logistics partners to warehousing and transportation routes. This visualization allows companies to better understand how each component of the supply chain interacts with others, helping to identify potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies. For instance, by using graph technology, businesses can quickly pinpoint which suppliers are most crucial to their operations and what impact a disruption might have across the entire network.
2. Uncover hidden relationships and optimizing paths
Graph databases are ideal for revealing relationships that aren’t immediately apparent in traditional relational databases. For example, graph databases can uncover connections between suppliers and distribution routes that may otherwise go unnoticed. This capability allows businesses to optimize delivery routes, find alternative suppliers, and anticipate supply chain disruptions before they occur. By running predictive analytics and what-if scenarios on these networks, companies can forecast demand, adjust inventory levels, and optimize production schedules in real time.
3. Enhancing decision-making with predictive analytics
Graph technology plays a crucial role in enabling businesses to leverage predictive analytics for better demand forecasting and decision-making. By analyzing the relationships between supply chain nodes, graph databases help companies predict how disruptions—such as a supplier shortage or a natural disaster—might ripple through the supply chain. This enables faster responses to unforeseen events and allows for more strategic planning in areas like inventory management and procurement.
4. Access real-time data analysis for agility and responsiveness
One of the key advantages of graph technology is its ability to process real-time data, providing companies with the agility and responsiveness needed to navigate today’s rapidly changing business landscape. By continuously analyzing and updating the relationships within the supply chain, businesses can respond to disruptions in real time, reroute shipments, adjust inventory levels, and manage supplier risks more effectively. This real-time decision-making capability is essential for companies looking to maintain a competitive edge and build more resilient supply chains.
Use Cases of Graph Technology in SCM
1. Agriculture supply chain
Rishi Pethe, in the Future of Agriculture podcast, highlights how knowledge graphs can incorporate both structured (for example, data coming from a spreadsheet or precision agriculture equipment) and unstructured data (e.g., a Twitter feed, images, YouTube video, bulletin board information, books, etc.) data in agriculture.
“Building a data set of crops and varieties is a necessary and an early step to building a valuable knowledge graph in agriculture,” says Pethe. He notes that “knowledge graphs can be successful and valuable if they can uncover new insights by automatically incorporating new data sources, understanding the context, finding new connections, and continuously evolving.”
2. Food supply chain
According to research in the food industry, knowledge graphs in the food supply chain improve data integration, traceability, and decision-making by connecting diverse data sources, such as IoT devices, nutrition databases, and social media. This approach helps solve challenges like contamination traceability, food quality assessment, and optimizing supply chains by standardizing data and linking related information. As a result, knowledge graphs enable a more efficient and intelligent “Internet of Food,” enhancing transparency and operational efficiency across the entire food system.
3. Automotive industry
To overcome challenges in its product validation life cycle, where siloed data across teams slowed down vehicle development, a major Japanese automotive manufacturer used Neo4j graph technology. By implementing a knowledge graph, the company standardized its test data, making it reusable and accessible across the entire organization.
“With the help of Neo4j and BRIX PVM, we’ve built a knowledge graph that can incorporate well-defined semantics for tests, subtests, and measurements in a unified manner. We’re capturing the knowledge of an expert engineer,” said an engineer on the project.
The company’s engineers can now more quickly identify the root causes of issues and collaborate across domains, ultimately reducing the time to market for new vehicles.
4. Military logistics
The U.S. Army faced challenges managing the massive amount of data related to equipment maintenance and spare parts procurement. By adopting Neo4j, the Army can now query large datasets with over 5.2 billion nodes and 14.1 billion relationships, providing real-time visibility into the cost and availability of spare parts.
“Typically it would take 60 person-hours to load data so the Army could understand ‘we’re going to need to replace X, Y, or Z parts’ or provide cost estimates and analyses,” said Hendrickson. “Now it’s down to seven to eight hours.”
5. Procurement optimization
By leveraging the database and analytics capabilities of Neo4j, Scoutbee enables companies like Unilever, Siemens, and Audi to visualize supplier interdependencies and optimize partnerships in real time.
“We offer 360-degree supplier views — we’re not just looking at a supplier from one data perspective, but bringing in all the data we have on a supplier and revealing the entire spectrum of relationships between them,” says Nischal Padmanabha, VP of Data and ML at Scoutbee.
Supplier discovery isn’t just more powerful with Neo4j, it’s also 75 percent faster and 85 percent less labor-intensive. Instead of spending 100-180 working hours over 24 weeks, Scoutbee clients now spend 8-12 hours over six weeks.
Future Trends in Supply Chain Management and Optimization
In the future, supply chain optimization will be shaped by advanced technologies like AI, blockchain, and IoT, along with a focus on sustainability. AI and machine learning will enable businesses to predict disruptions, automate processes, and make smarter decisions. Meanwhile, blockchain enhances transparency and security by providing a shared, immutable ledger of transactions, and IoT devices allow for real-time monitoring of goods throughout the supply chain.
Graph technology also plays a key role by offering real-time visibility into complex supply chain networks, allowing companies to analyze relationships and dependencies across suppliers, logistics, and operations. This deeper insight enables faster, smarter decision-making and enables greater optimization of the modern supply chain.
End-to-End Supply Chain Visibility With a Knowledge Graph
Unify your data to build a resilient supply chain. Discover dependencies you didn’t know existed, spot risks, and make smarter decisions.