Load JDBC (RDBMS)
Data Integration is an important topic. Reading data from relational databases to create and augment data models is a very helpful exercise.
With apoc.load.jdbc you can access any database that provides a JDBC driver, and execute queries whose results are turned into streams of rows.
Those rows can then be used to update or create graph structures.
| type | qualified name | signature | description |
|---|---|---|---|
procedure |
|
|
apoc.load.jdbc('key or url','table or statement', params, config) YIELD row - load from relational database, from a full table or a sql statement |
procedure |
|
|
deprecated - please use: apoc.load.jdbc('key or url','',[params]) YIELD row - load from relational database, from a sql statement with parameters |
procedure |
|
|
apoc.load.jdbcUpdate('key or url','statement',[params],config) YIELD row - update relational database, from a SQL statement with optional parameters |
To simplify the JDBC URL syntax and protect credentials, you can configure aliases in conf/apoc.conf:
apoc.jdbc.myDB.url=jdbc:derby:derbyDB
CALL apoc.load.jdbc('jdbc:derby:derbyDB','PERSON')becomes
CALL apoc.load.jdbc('myDB','PERSON')The 3rd value in the apoc.jdbc.<alias>.url= effectively defines an alias to be used in apoc.load.jdbc('<alias>',….
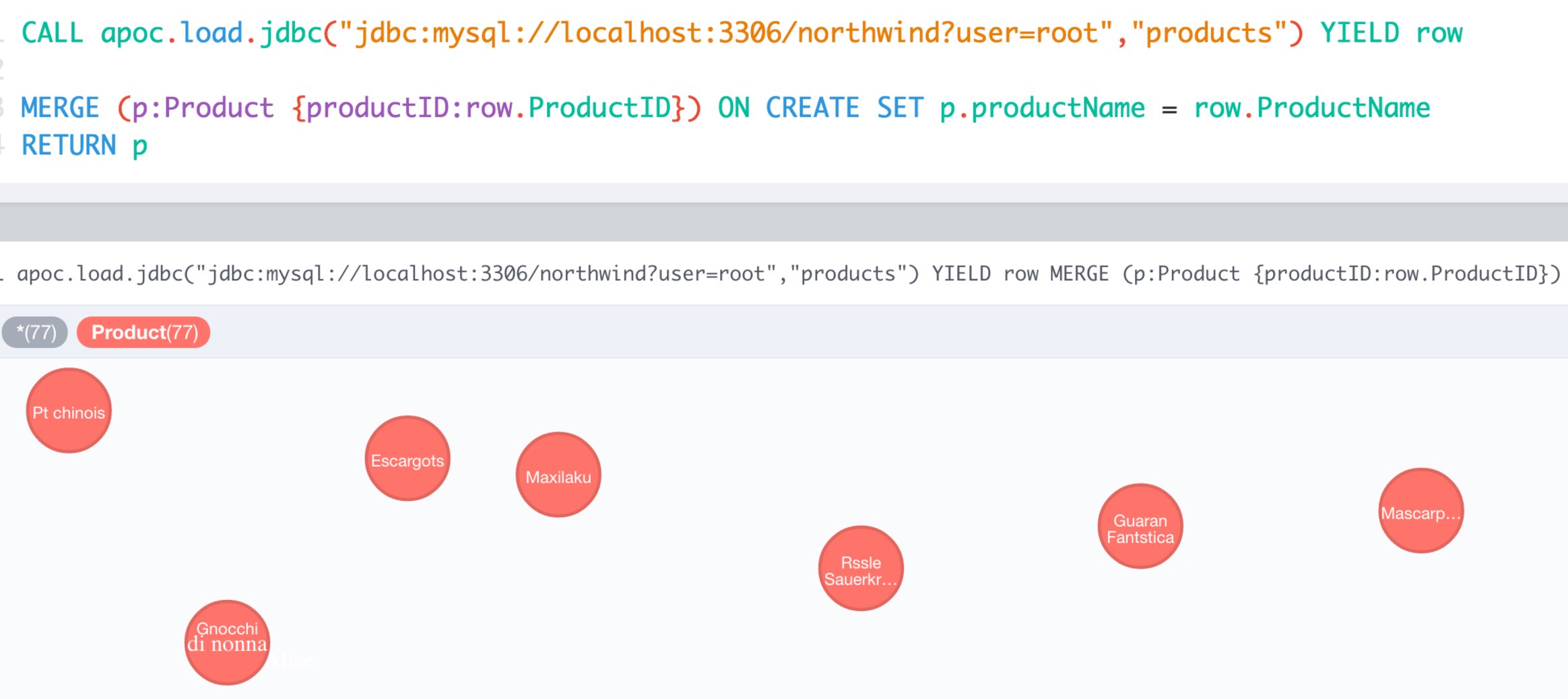
MySQL Example
Northwind is a common example set for relational databases, which is also covered in our import guides, e.g. :play northwind graph in the Neo4j browser.
MySQL Northwind Data
select count(*) from products;| count(*) |
|---|
77 |
describe products;| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ProductID |
int(11) |
NO |
PRI |
NULL |
auto_increment |
ProductName |
varchar(40) |
NO |
MUL |
NULL |
|
SupplierID |
int(11) |
YES |
MUL |
NULL |
|
CategoryID |
int(11) |
YES |
MUL |
NULL |
|
QuantityPerUnit |
varchar(20) |
YES |
NULL |
||
UnitPrice |
decimal(10,4) |
YES |
0.0000 |
||
UnitsInStock |
smallint(2) |
YES |
0 |
||
UnitsOnOrder |
smallint(2) |
YES |
0 |
||
ReorderLevel |
smallint(2) |
YES |
0 |
||
Discontinued |
bit(1) |
NO |
b'0' |
Load JDBC Examples
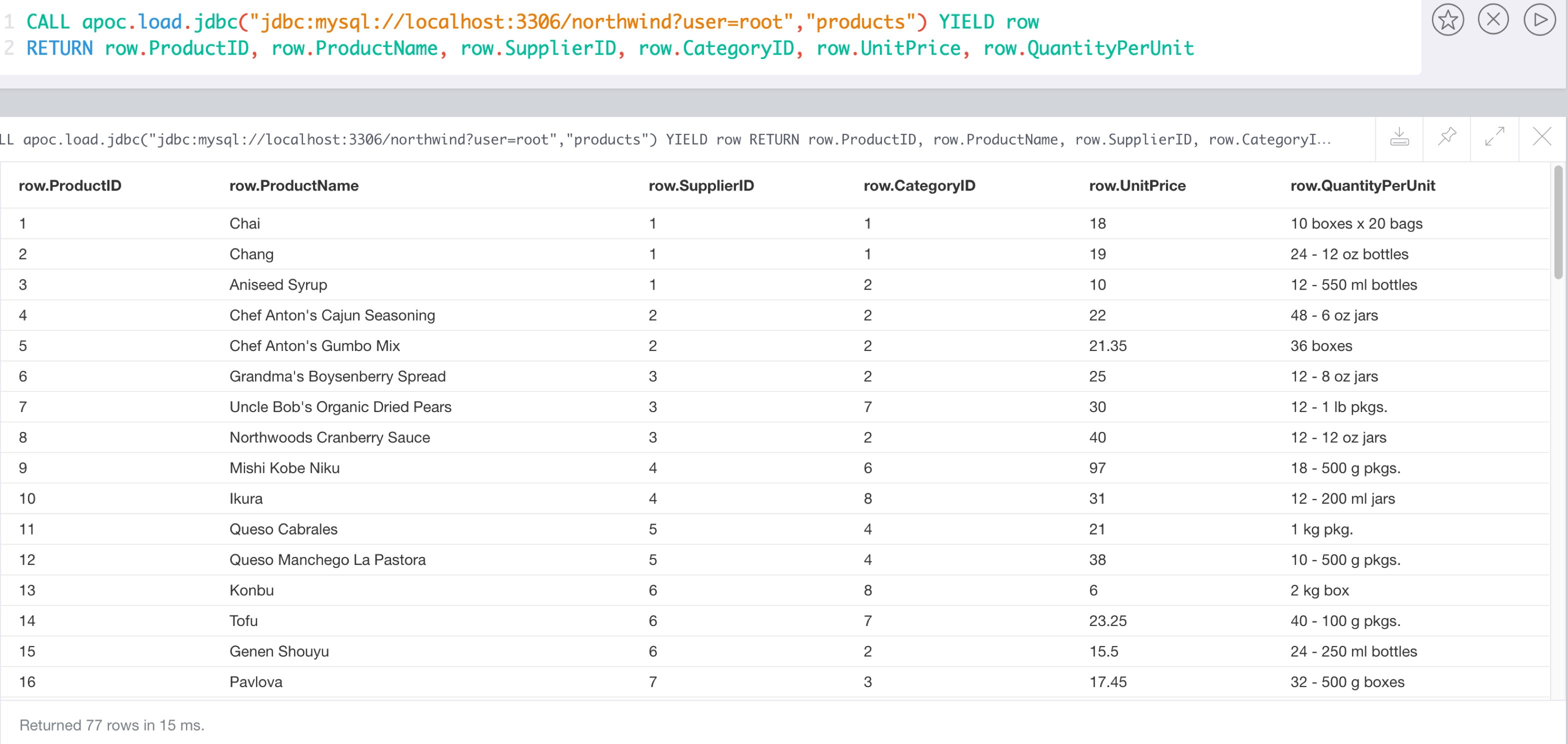
CALL apoc.load.driver("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");WITH "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/northwind?user=root" as url
CALL apoc.load.jdbc(url,"products") YIELD row
RETURN count(*);| count(*) |
|---|
77 |
WITH "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/northwind?user=root" as url
CALL apoc.load.jdbc(url,"products") YIELD row
RETURN row limit 1;| row |
|---|
{UnitPrice → 18.0000, UnitsOnOrder → 0, CategoryID → 1, UnitsInStock → 39} |
Load JDBC with params Examples
WITH "select firstname, lastname from employees where firstname like ? and lastname like ?" as sql
CALL apoc.load.jdbcParams("northwind", sql, ['F%', '%w'])
YIELD row
RETURN rowJDBC pretends positional "?" for parameters, so the third apoc parameter has to be an array with values coherent with that positions. In case of 2 parameters, firstname and lastname ['firstname-position','lastname-position']
Load data in transactional batches
You can load data from jdbc and create/update the graph using the query results in batches (and in parallel).
CALL apoc.periodic.iterate(
'CALL apoc.load.jdbc("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/northwind?user=root","company")',
'CREATE (p:Person) SET p += value',
{ batchSize:10000, parallel:true})
RETURN batches, totalCassandra Example
Setup Song database as initial dataset
curl -OL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/neo4j-contrib/neo4j-cassandra-connector/master/db_gen/playlist.cql curl -OL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/neo4j-contrib/neo4j-cassandra-connector/master/db_gen/artists.csv curl -OL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/neo4j-contrib/neo4j-cassandra-connector/master/db_gen/songs.csv $CASSANDRA_HOME/bin/cassandra $CASSANDRA_HOME/bin/cqlsh -f playlist.cql
Download the Cassandra JDBC Wrapper, and put it into your $NEO4J_HOME/plugins directory.
Add this config option to $NEO4J_HOME/conf/apoc.conf to make it easier to interact with the cassandra instance.
apoc.jdbc.cassandra_songs.url=jdbc:cassandra://localhost:9042/playlist
Restart the server.
Now you can inspect the data in Cassandra with.
CALL apoc.load.jdbc('cassandra_songs','artists_by_first_letter')
YIELD row
RETURN count(*);| count(*) |
|---|
3605 |
CALL apoc.load.jdbc('cassandra_songs','artists_by_first_letter')
YIELD row
RETURN row LIMIT 5;CALL apoc.load.jdbc('cassandra_songs','artists_by_first_letter')
YIELD row
RETURN row.first_letter, row.artist
LIMIT 5;| row.first_letter | row.artist |
|---|---|
C |
C.W. Stoneking |
C |
CH2K |
C |
CHARLIE HUNTER WITH LEON PARKER |
C |
Calvin Harris |
C |
Camané |
Let’s create some graph data, we have a look at the track_by_artist table, which contains about 60k records.
CALL apoc.load.jdbc('cassandra_songs','track_by_artist')
YIELD row
RETURN count(*);CALL apoc.load.jdbc('cassandra_songs','track_by_artist')
YIELD row
RETURN row
LIMIT 5;CALL apoc.load.jdbc('cassandra_songs','track_by_artist')
YIELD row
RETURN row.track_id, row.track_length_in_seconds, row.track, row.music_file, row.genre, row.artist, row.starred
LIMIT 2;| row.track_id | length | row.track | row.music_file | row.genre | row.artist | row.starred |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
c0693b1e-0eaa-4e81-b23f-b083db303842 |
219 |
1913 Massacre |
TRYKHMD128F934154C |
folk |
Woody Guthrie & Jack Elliott |
false |
7d114937-0bc7-41c7-8e0c-94b5654ac77f |
178 |
Alabammy Bound |
TRMQLPV128F934152B |
folk |
Woody Guthrie & Jack Elliott |
false |
Let’s create some indexes and constraints, note that other indexes and constraints will be dropped by this.
CALL apoc.schema.assert(
{Track:['title','length']},
{Artist:['name'],Track:['id'],Genre:['name']});| label | key | unique | action |
|---|---|---|---|
Track |
title |
false |
CREATED |
Track |
length |
false |
CREATED |
Artist |
name |
true |
CREATED |
Genre |
name |
true |
CREATED |
Track |
id |
true |
CREATED |
CALL apoc.load.jdbc('cassandra_songs','track_by_artist')
YIELD row
MERGE (a:Artist {name:row.artist})
MERGE (g:Genre {name:row.genre})
CREATE (t:Track {id:toString(row.track_id), title:row.track, length:row.track_length_in_seconds})
CREATE (a)-[:PERFORMED]->(t)
CREATE (t)-[:GENRE]->(g);Added 63213 labels, created 63213 nodes, set 182413 properties, created 119200 relationships, statement executed in 40076 ms.
Support for Hive with Kerberos Auth
Support for Hive especially with Kerberos is more involved.
First of all the required configuration is more detailed, make sure to get this information:
-
kerberos user / password
-
kerberos realm / kdc
-
hive hostname + port (10000)
Create this login.conf file at a known location:
KerberosClient {
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required
debug=true debugNative=true;
};
Add these options to your conf/apoc.conf
dbms.jvm.additional=-Djava.security.auth.login.config=/path/to/login.conf dbms.jvm.additional=-Djava.security.auth.login.config.client=KerberosClient dbms.jvm.additional=-Djava.security.krb5.realm=KRB.REALM.COM dbms.jvm.additional=-Djava.security.krb5.kdc=krb-kdc.host.com
Unlike other JDBC drivers, Hive comes with a bunch of dependencies, you can download these from the Hadoop providers
or grab them from maven central.
The versions might vary, use what comes with your Hive driver.
-
hadoop-common-2.7.3.2.6.1.0-129.jar
-
hive-exec-1.2.1000.2.6.1.0-129.jar
-
hive-jdbc-1.2.1000.2.6.1.0-129.jar
-
hive-metastore-1.2.1000.2.6.1.0-129.jar
-
hive-service-1.2.1000.2.6.1.0-129.jar
-
httpclient-4.4.jar
-
httpcore-4.4.jar
-
libfb303-0.9.2.jar
-
libthrift-0.9.3.jar
Now you can use a JDBC URL like this from APOC.
| This has no newlines, it’s just wrapped because it is too long. |
jdbc:hive2://username%40krb-realm:password@hive-hostname:10000/default;principal=hive/hostname@krb-realm;auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject
And then call:
WITH 'jdbc:hive2://username%40krb-realm:password@hive-hostname:10000/default;principal=hive/hostname@krb-realm;auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject' AS url
CALL apoc.load.jdbc(url,'PRODUCTS')
YIELD row
RETURN row.name, row.price;You can also set it in your conf/apoc.conf as a key:
apoc.jdbc.my-hive.url=jdbc:hive2://username%40krb-realm:password@hive-hostname:10000/default;principal=hive/hostname@krb-realm;auth=kerberos;kerberosAuthType=fromSubject
And then use the more compact call:
CALL apoc.load.jdbc('my-hive','SELECT * PRODUCTS');LOAD JDBC - Resources
To use other JDBC drivers use these download links and JDBC URL.
Put the JDBC driver into the $NEO4J_HOME/plugins directory and configure the JDBC-URL in $NEO4J_HOME/conf/apoc.conf with apoc.jdbc.<alias>.url=<jdbc-url>
Credentials can be passed in two ways:
-
into url
CALL apoc.load.jdbc('jdbc:derby:derbyDB;user=apoc;password=Ap0c!#Db;create=true', 'PERSON')-
by config parameter.
CALL apoc.load.jdbc('jdbc:derby:derbyDB', 'PERSON',[],{credentials:{user:'apoc',password:'Ap0c!#Db'}})| Database | JDBC-URL | Driver Source |
|---|---|---|
MySQL |
|
|
Postgres |
|
|
Oracle |
|
|
MS SQLServer |
|
|
IBM DB2 |
|
|
Derby |
|
Included in JDK6-8 |
Cassandra |
|
|
SAP Hana |
|
|
Apache Hive (w/ Kerberos) |
|
Apache Hive Driver (Cloudera) (Hortonworks) There are several jars (hadoop-common-xxx.jar hive-exec-xxx.jar hive-jdbc-xxx.jar hive-metastore-xxx.jar hive-service-xxx.jar httpclient-4.4.jar httpcore-4.4.jar libfb303-0.9.2.jar libthrift-0.9.3.jar) |
There are a number of blog posts / examples that details usage of apoc.load.jdbc
LOAD JDBC - UPDATE
The jdbcUpdate is use for update relational database, from a SQL statement with optional parameters
CALL apoc.load.jdbcUpdate(jdbc-url,statement, params, config)With this set of data you can call the procedure in two different mode:
MATCH (u:User)-[:BOUGHT]->(p:Product)<-[:BOUGHT]-(o:User)-[:BOUGHT]->(reco)
WHERE u <> o AND NOT (u)-[:BOUGHT]->(reco)
WITH u, reco, count(*) as score
WHERE score > 1000You can call the procedure with param:
CALL apoc.load.jdbcUpdate('jdbc:mysql:....','INSERT INTO RECOMMENDATIONS values(?,?,?)',[user.id, reco.id, score]);You can call the procedure without param:
CALL apoc.load.jdbcUpdate('jdbc:mysql:....','INSERT INTO RECOMMENDATIONS values(user.id, reco.id, score)');Load JDBC format date
Starting from Neo4j 3.4 there is the support for Temporal Values
If the returning JdbcType, from the load operation, is TIMESTAMP or TIMESTAMP_WITH_TIMEZONE you could provide the configuration parameter timezone with type java.time.ZoneId
CALL apoc.load.jdbc('key or url','table or statement', config);Config
Config param is optional, the default value is an empty map.
|
default value: null |
|
default value: {} |
Example:
CALL apoc.load.jdbc(
'jdbc:derby:derbyDB',
'SELECT * FROM PERSON WHERE NAME = ?',['John'],
{timezone: "Asia/Tokyo"})2018-10-31T01:32:25.012+09:00[Asia/Tokyo]
CALL apoc.load.jdbcUpdate('jdbc:derby:derbyDB','UPDATE PERSON SET NAME = ? WHERE NAME = ?',['John','John'],{credentials:{user:'apoc',password:'Ap0c!#Db'}})CALL apoc.load.jdbc('jdbc:derby:derbyDB', 'PERSON',[],{credentials:{user:'apoc',password:'Ap0c!#Db'}})