Next-Generation Neo4j Hosting on AWS with GrapheneDB

Founder of GrapheneDB
6 min read
GrapheneDB is a Bronze sponsor of GraphConnect San Francisco. Meet their team on October 13-14th at the Hyatt Regency SF.
With the Neo4j community gearing up for GraphConnect San Francisco – the most important event in the graph database ecosystem – we’d like to review the most notable recent improvements in Neo4j and GrapheneDB.
At GrapheneDB, we have been operating Neo4j databases in the cloud since 2013. We have seen first-hand how Neo4j has improved over time, enhancing its performance, stability and user-facing features.
Neo4j 3.0 was released earlier this year, and Neo4j 3.1 is likely to be released soon.
If you’re reading this and you haven’t started using Neo4j 3.0 yet, I encourage you to give it a try. Download the latest Neo4j 3.x release or take Neo4j 3.0 on GrapheneDB for a spin.
New in Neo4j
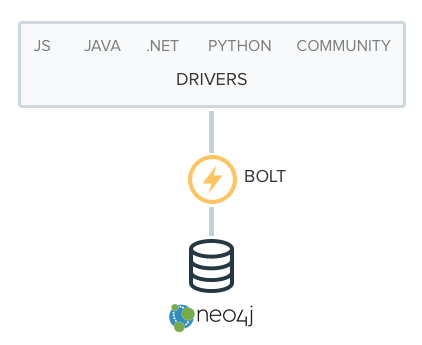
New Bolt Binary Protocol and Drivers
The new Bolt protocol is probably Neo4j’s most notable improvement since the introduction of the Neo4j Browser interface in Neo4j 2.0 and the graph query language Cypher. GrapheneDB supports Bolt out of the box on all Neo4j versions 3.0 and higher.
Bolt is a new, lightweight binary protocol that provides a blazing fast interface and aims to do so consistently, regardless of the programming language on the client side.
Before Bolt, JVM languages would benefit from top performance while others were treated as second-class citizens. With Bolt, everybody can enjoy a uniform, fast interface.
High Performance over the Network
The use of persistent network connections in Bolt results in less time spent establishing new HTTP connections. In contrast to HTTP REST, the Bolt protocol requires session initialization, but after that, multiple queries can be sent within the same session.
The binary nature of Bolt’s protocol also provides a much smaller footprint than the JSON format used in the HTTP REST interface. In addition, query results are always streamed over the wire so the client can start fetching them as they are returned.
All of these characteristics of Bolt result in notable performance improvements compared to the Neo4j’s pre-existing REST API. If you’re ever had to hack solutions to achieve high throughputs in critical scenarios, like drop down to the Java API, use unmanaged server extensions, or run Neo4j in embedded mode, it’s safe to say that moving forward this way won’t be necessary anymore.
Officially Maintained Language Drivers
Alongside the release of Bolt, the Neo4j teams has also introduced a range of new language drivers that are now officially maintained. Because Bolt is an open protocol standard, there will always be numerous options when it comes to connecting an app or server to Neo4j.
Picking one of the official drivers means less friction in getting your app to integrate with Neo4j and less risk of running into complications when upgrading to future versions of Neo4j. Other drivers will continue to deliver additional functionalities or interface flavors, which some developers might find convenient based on their preferences.
You can check out the list of currently available official drivers in the Neo4j developer documentation.
New in GrapheneDB
Stored Procedures
At GrapheneDB, we’ve always believed that the extensibility of Neo4j was one of its strengths. We have worked with many customers who have relied on unmanaged server extensions or plugins to extend Neo4j.
In addition to supporting Neo4j plugins and extensions for years, GrapheneDB also recently added support for custom stored procedures.
With stored procedures, users can now extend Neo4j by writing custom code that can be invoked directly from Cypher. This opens up many opportunities.
Whereas plugins and extensions previously required separate HTTP REST requests and responses, users can now benefit from one single interface, and fully integrated custom logic within Cypher.
For example, stored procedures can be helpful in cases that involve:
- Implementing logic that is better suited for the imperative paradigm, such as custom traversal algorithms
- Difficulties expressing a query in Cypher
- Performing global operations on the graph
- Extending Cypher with a custom feature
Since these custom stored procedure extensions are available within the Cypher execution engine, users can take advantage of procedures from Bolt directly without having to use HTTP.
Next-Generation Neo4j Hosting on AWS
Having operated Neo4j production instances for customers since 2013, we have been able to learn about the challenges developers face when deploying and operating applications. The experiences we have collected on our journey have played a major role in how we shape our service, and in the value we ultimately strive to provide to our customers.
In addition to introducing support for Bolt and stored procedures, most of our engineering efforts have been targeted at improving the developer experience and making sure we help our customers succeed.
Better Visibility into Neo4j Performance
We have learned that while the graph model and the Cypher query language are extremely powerful and flexible, it’s often times challenging to understand how to best model or query your graph. Mistakes in data modeling, indexing or querying can result in poor response times or database unresponsiveness, which are ultimately damaging to the developer experience and business operations.
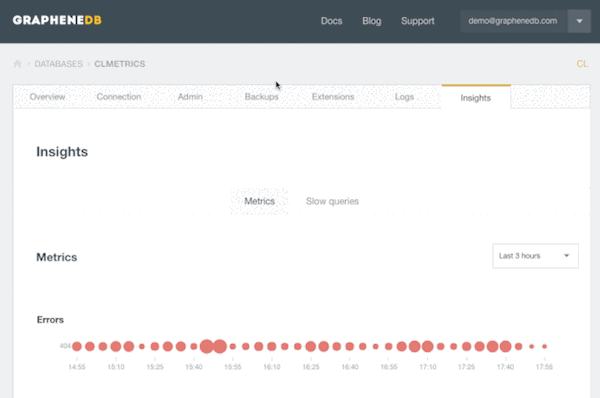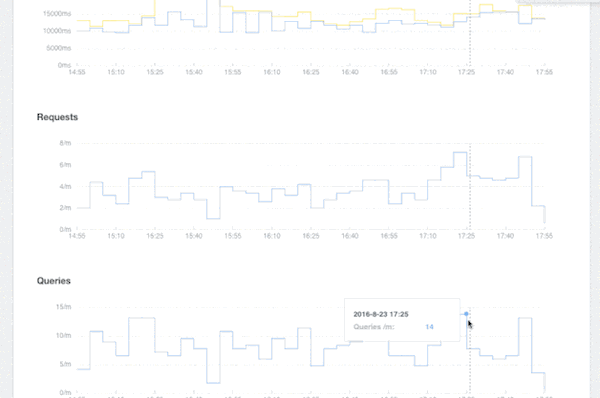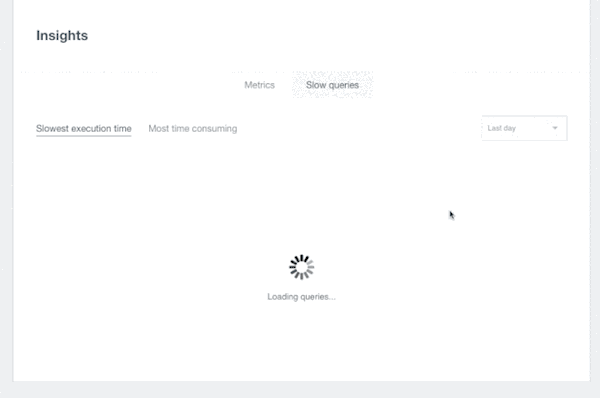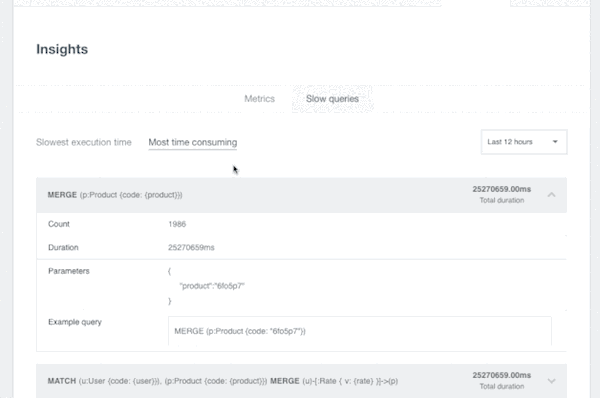
In an effort to provide more visibility into Neo4j performance issues and help users identify and solve them, we have been working on our Insights feature suite. The Insights suite currently includes two features: metrics and slow queries (currently in beta).
Metrics provides visibility into Neo4j’s performance, including median and 95th percentile response times, query and request throughput volumes and individual error rates, over different time windows (last hour, three hours, 12 hours, etc.).
Insights also provides visibility into the slowest and most time-consuming queries in your Neo4j database for specific time windows.
All queries that hit the database are registered after normalizing them (by extracting parameters from non-parametrized queries and treating them as if they were parametrized). By doing so, Insights’ slow queries feature can group instances of the same query together and aggregate the response times during a given time window.
The results are displayed as the slowest queries (highest median and 95th percentile response times) and the most time consuming (think highest median multiplied by the number of executions).
Insights Metrics is a great tool to use when changes are introduced (e.g., new queries) or when things are starting to go wrong (e.g., errors on the client side). Based on the information provided, the user can determine whether the issues are due to external factors (e.g., traffic spike) or caused by queries.
If the problem is caused by queries, Insights Slow Queries will pinpoint the queries that are causing trouble.
You can read more about metrics in this announcement. Stay tuned for the upcoming announcement when the Insights package is released.
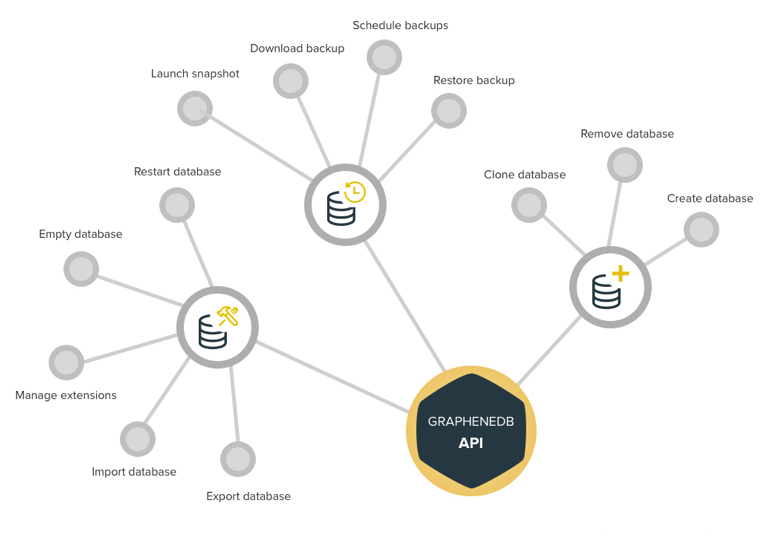
Neo4j Database Management through API
At GrapheneDB we have always been huge fans of AWS and Heroku and love how APIs enable developers to create new processes and tools. The API revolution is transforming the way in which software is written and deployed and creating opportunities for new business models.
GrapheneDB customers have frequently asked for an API to perform database management and operational tasks automatically. We have been working closely with them and as a result are now proud to announce our upcoming public API.
The new GrapheneDB API seamlessly facilitates Neo4j operational database management from scripts and applications.
So far, we have seen our API help with some interesting use cases, including the following:
- Syncing different environments periodically, such as restoring the QA database with a fresh copy of production every day
- Deploying databases, stored procedures or extensions from automated tests or code branches
- Automatically downloading all production database backups onto your infrastructure for business continuity
- Developing SaaS products that require one individual database per account
We are excited about our new API. Watch for the release announcement and reach out if you have questions or comments or if you want to be one of the first developers to know when the API goes live.
Conclusions
Neo4j 3.0 is a game changer in terms of performance, because of the new binary protocol Bolt, and extensibility, due to the new stored procedures.
GrapheneDB lets developers unleash the full potential of Neo4j 3.0 in the cloud. As the world’s first fully managed Neo4j cloud-hosting service we take graph operability and automations to the next level with our new Insights and API features.
Check out our website to learn more about GrapheneDB’s Neo4j hosting options on Amazon Web Services (AWS).
If you are attending GraphConnect 2016 in San Francisco on October 13, please stop by our booth to discuss graphs and cloud, or simply tell us about your exciting project.