Intro To GraphQL & Neo4j
Lesson Overview
In this lesson we take a look at GraphQL, Neo4j, and the Neo4j GraphQL Library. We explore GraphQL including important concepts for querying with GraphQL and building GraphQL API applications. We introduce the Neo4j GraphQL Library, a Node.js library that helps developers build GraphQL APIs backed by Neo4j.
What is Neo4j?
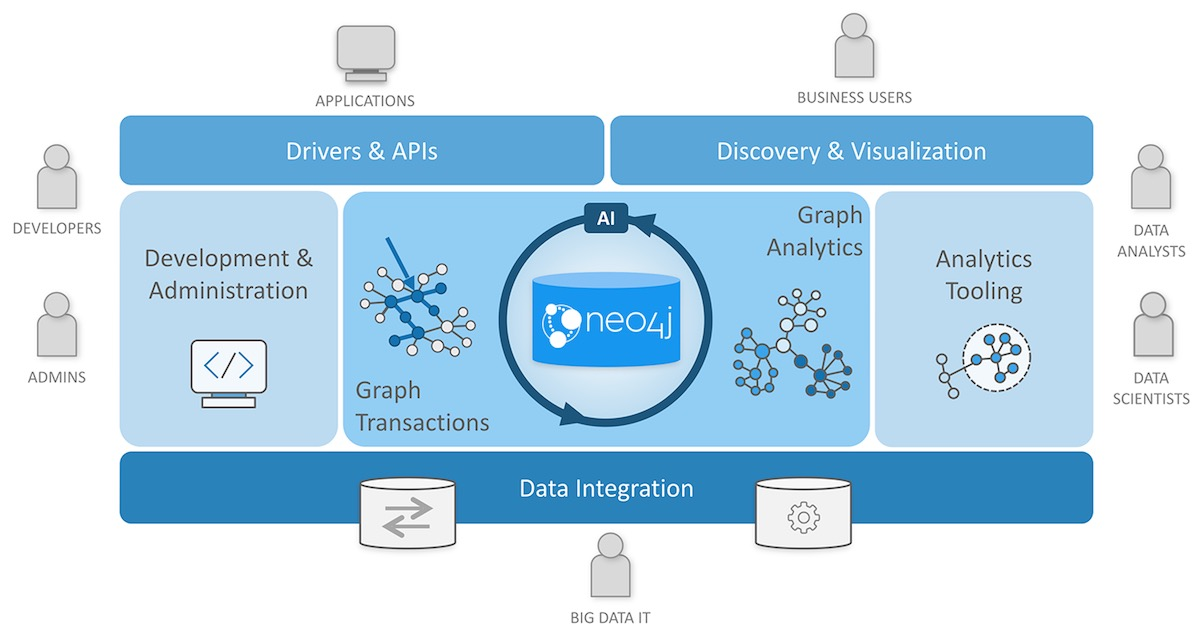
Neo4j is a native graph database with many features and functionality making up the Neo4j Graph Platform. Specifically:
-
The Neo4j DBMS
-
The property graph data model
-
The Cypher query language
-
Language drivers using the Bolt protocol for building applications
-
Graph analytics with Graph Data Science
-
Data visualization with Neo4j Bloom
-
Neo4j Aura database-as-a-service
-
A GraphQL integration for building GraphQL APIs backed by Neo4j
This course may be completed even if you don’t have much Neo4j experience, however we suggest reviewing the Neo4j Developer Guides for a better understanding of some of the features of the Neo4j graph database.
What is GraphQL?

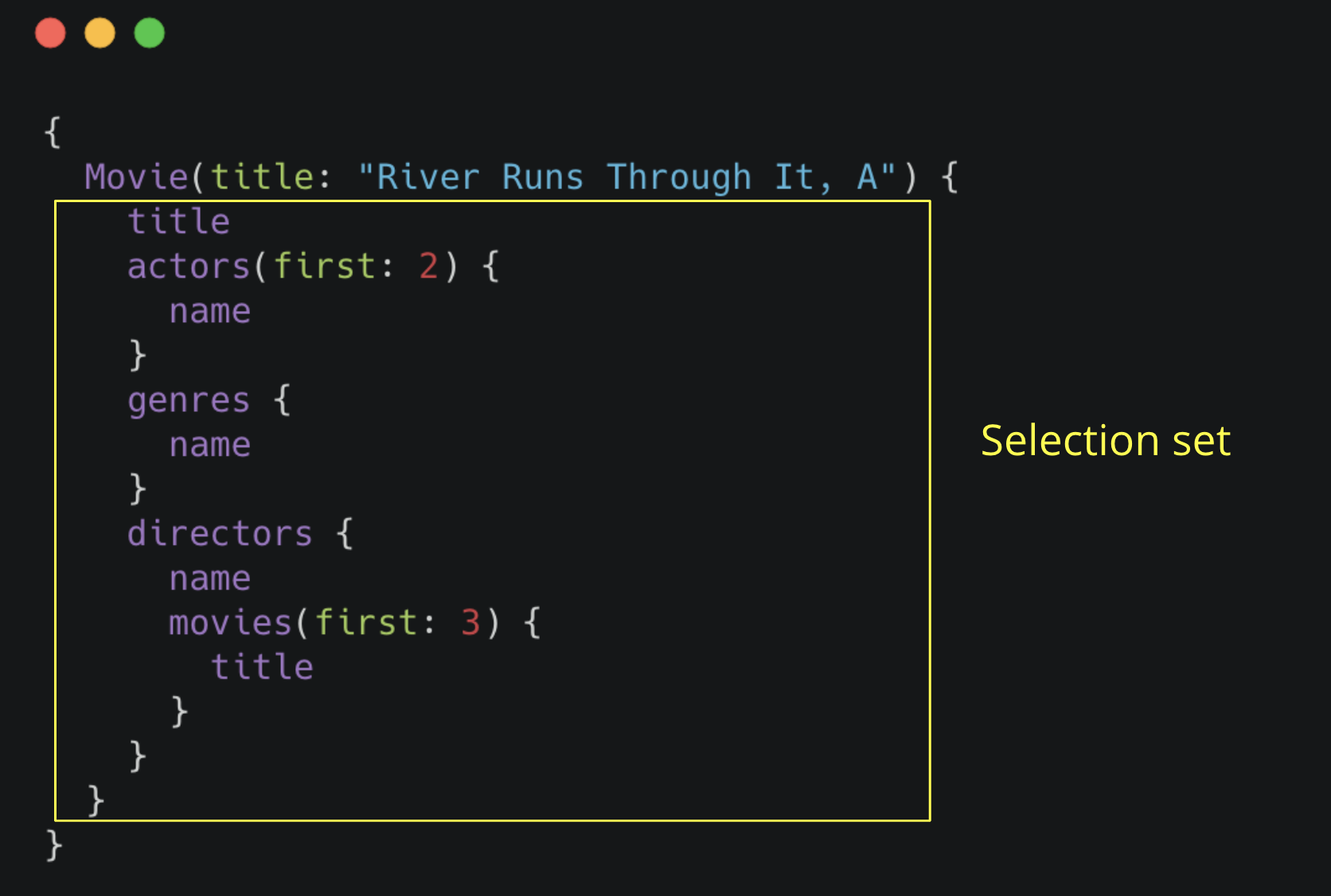
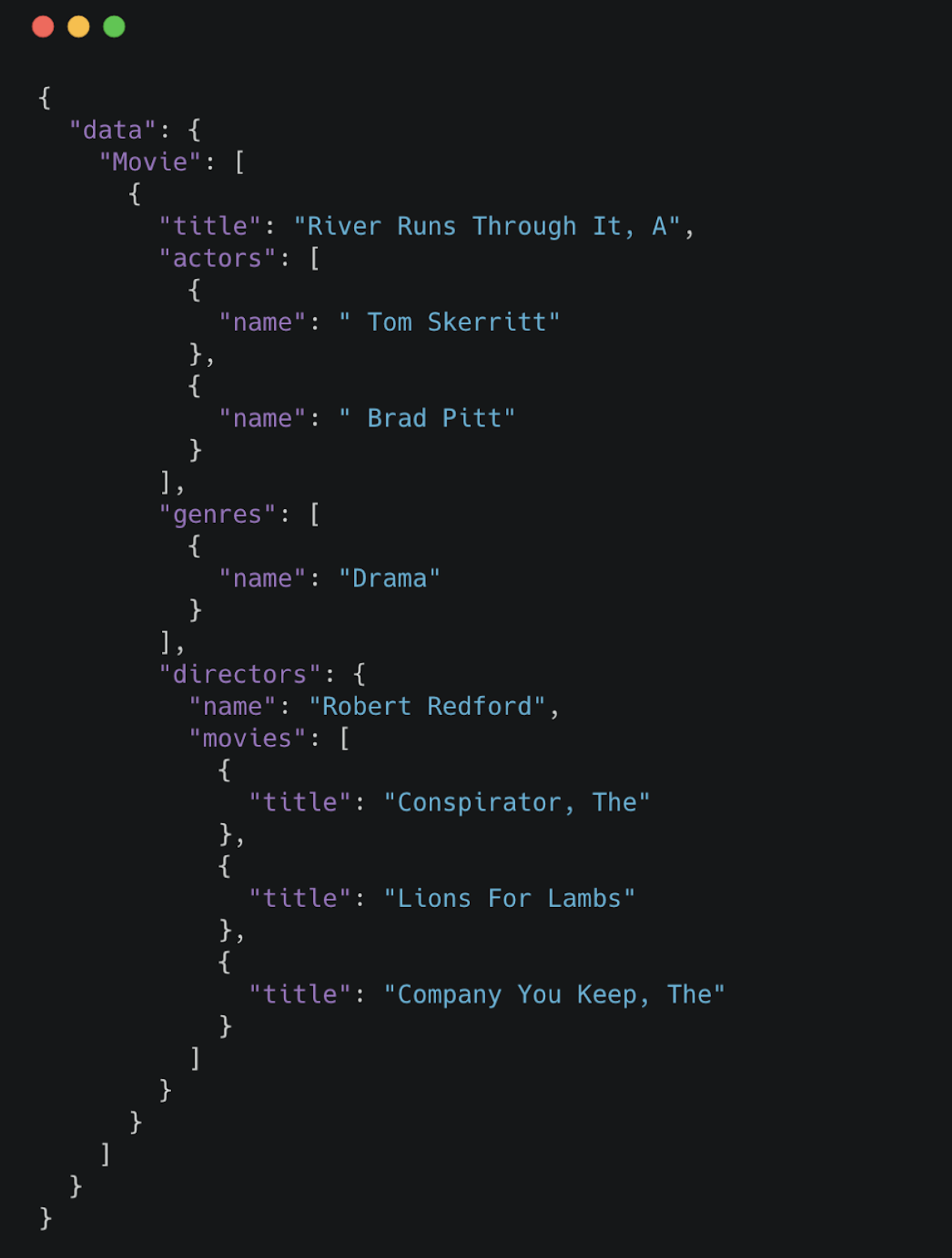
GraphQL is an API query language and runtime for fulfilling those queries. GraphQL uses a type system to define the data available in the API, including what entities and attributes (types and fields in GraphQL parlance) exist and how types are connected (the data graph). GraphQL operations (queries, mutations, or subscriptions) specify an entry-point and a traversal of the data graph (the selection set) which defines what fields to be returned by the operation. See the official GraphQL site for a more in-depth overview of GraphQL.
Important GraphQL Concepts
GraphQL Type Definitions
GraphQL type definitions define the data available in the API. These type definitions are typically defined using the GraphQL Schema Definition Language (SDL), a language-agnostic way of expressing the types. However, type definitions can be also be defined programmatically.
GraphQL Operations
Each GraphQL operation is either a Query, Mutation, or Subscription. The fields of the Query, Mutation, and Subscription types define the entry points for an operation. Each operation starts at the field of one of these types.

Benefits of GraphQL
Some of the benefits of GraphQL include:
-
Overfetching - sending less data over the wire
-
Underfetching - everything the client needs in a single request
-
The GraphQL specification defines exactly what GraphQL is
-
Simplify data fetching with component-based data interactions
-
"Graphs all the way down" - GraphQL can help unify disparate systems and focus API interactions on relationships instead of resources.
-
Developer productivity - By reasoning about application data as a graph with a strict type system, developers can focus on building applications.
GraphQL Challenges
Of course GraphQL is not a silver bullet. It’s important to be aware of some of the challenges that come from introducing GraphQL in a system.
-
Some well understood practices from REST don’t apply
-
HTTP status codes
-
Error handling
-
Caching
-
Exposing arbitrary complexity to the client and performance considerations
-
The n+1 query problem - the nested nature of GraphQL operations can lead to multiple requests to the data layer(s) to resolve a request
-
Query costing and rate limiting
Best practices and tooling have emerged to address all of the above, however it’s important to be aware of these challenges.
What is the Neo4j GraphQL Library?
The fundamental goal of the Neo4j GraphQL Library is to make it easier to build GraphQL APIs backed by Neo4j.
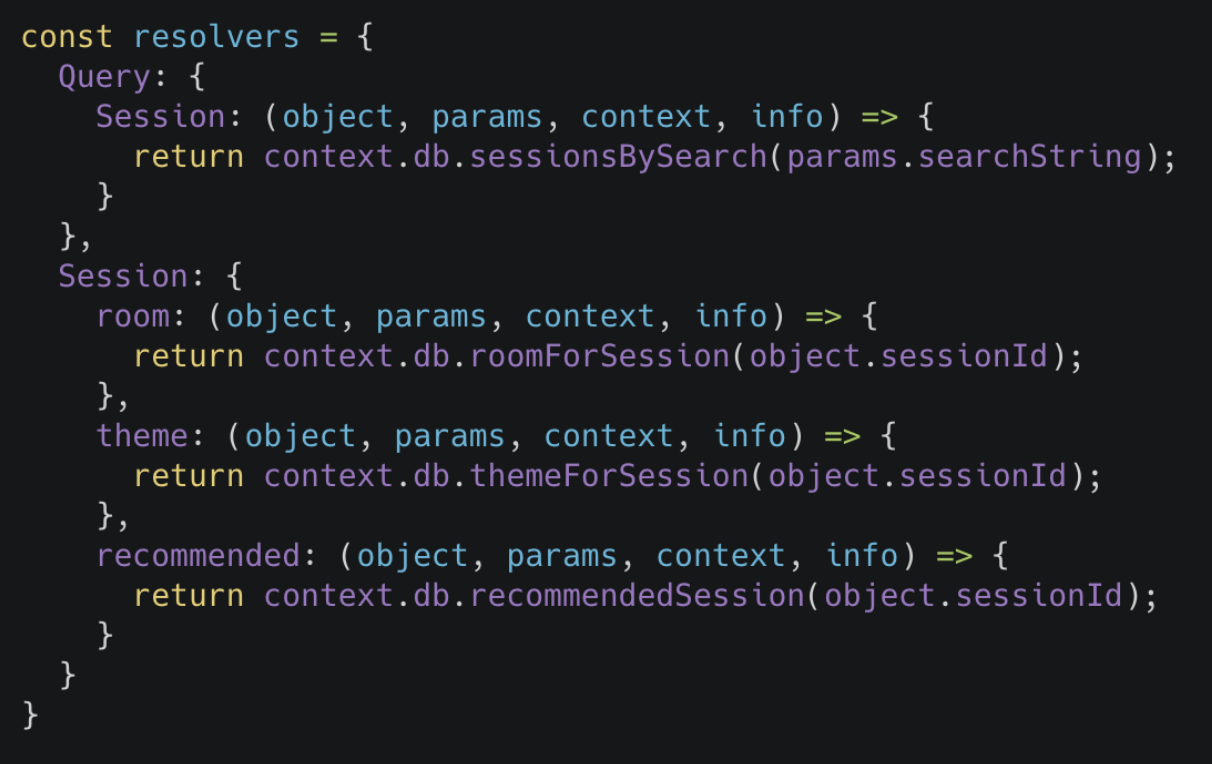
It’s important to point out that GraphQL is an API query language and NOT a database query language. The goal of the Neo4j GraphQL Library is to help build the API layer that sits between the client and database, not to execute GraphQL queries directly against the database.
At a high level, the goals of the Neo4j GraphQL Library are focused on:
-
Reducing boilerplate
-
Developer productivity
-
Extensibility
-
Performance
Goals of the Neo4j GraphQL Library
GraphQL First Development
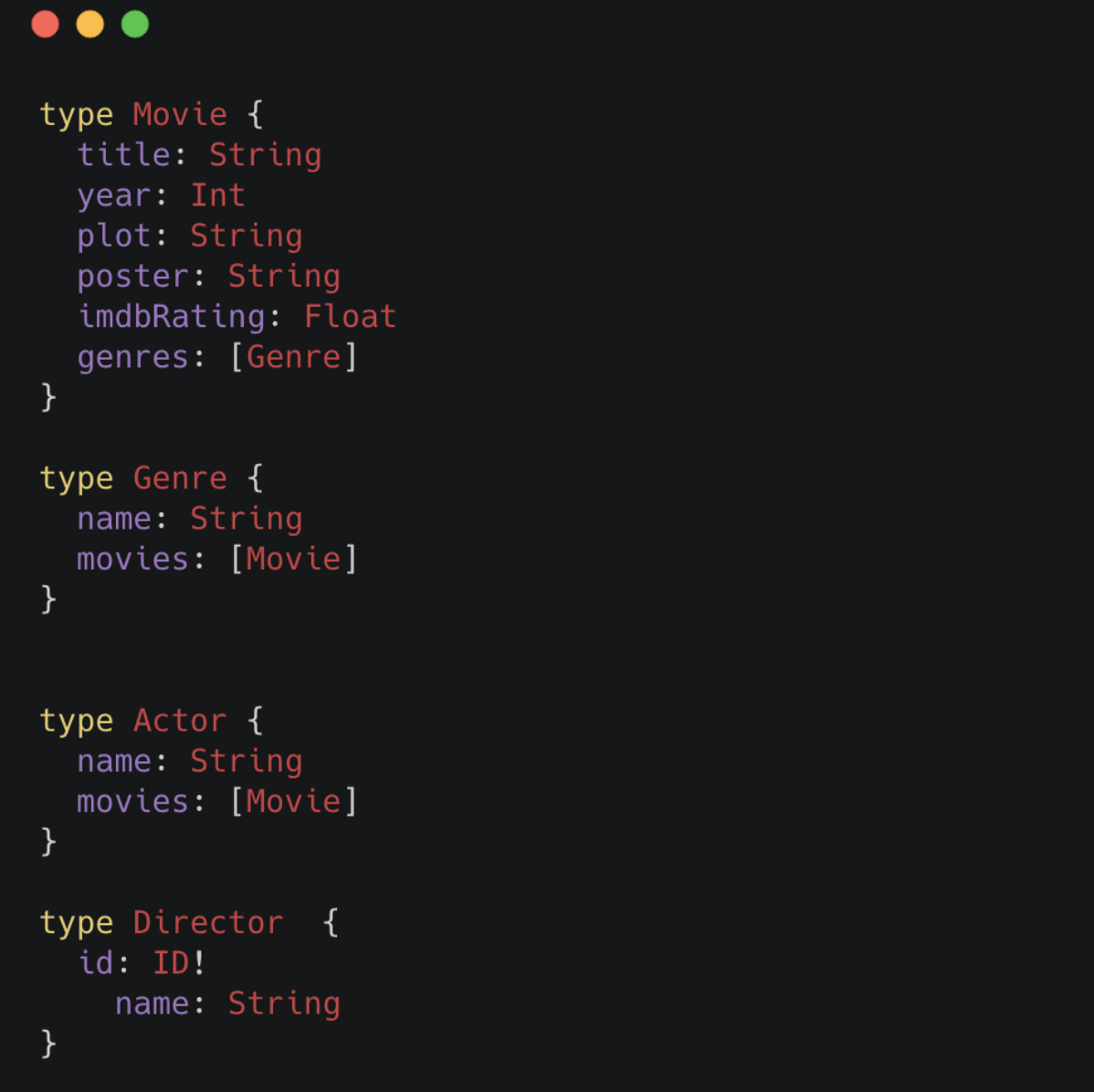
GraphQL type definitions can drive the database data model, which means we don’t need to maintain two separate schemas for our API and database.
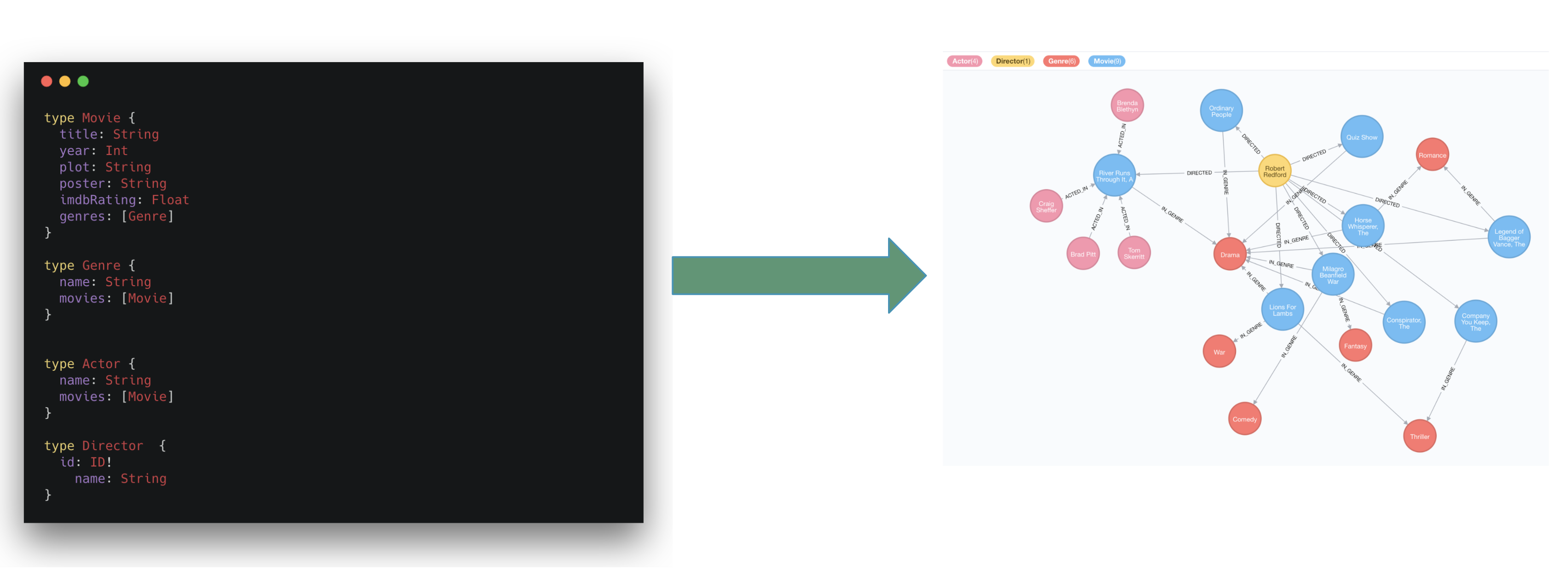
Auto-generate GraphQL API Operations
With the Neo4j GraphQL Library, GraphQL type definitions provide the starting point for a generated API that includes:
-
Query & Mutation types (an API entrypoint for each type defined in the schema)
-
Ordering
-
Pagination
-
Complex filtering
-
DateTime & Spatial types and filtering
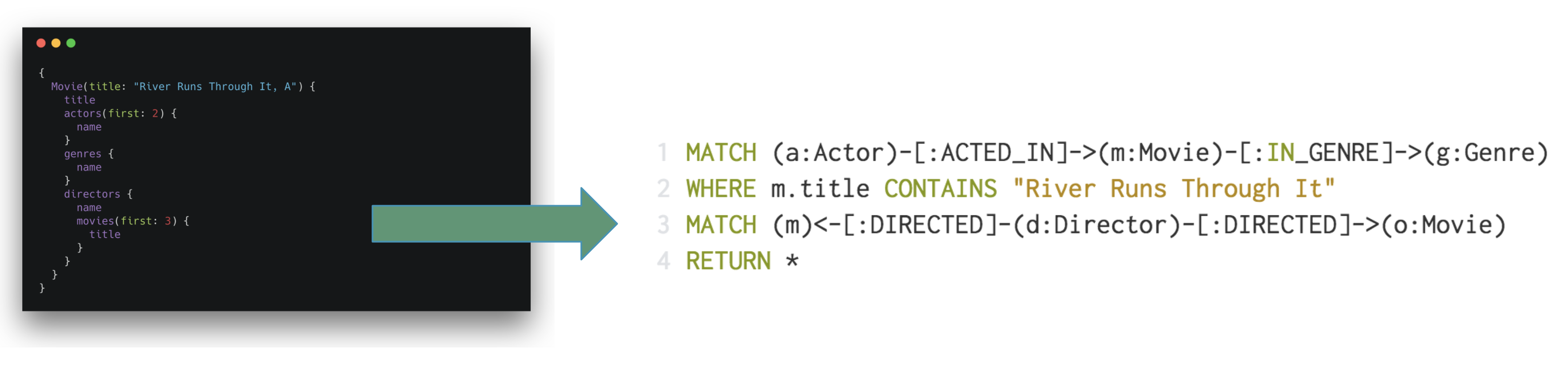
Generate Cypher From GraphQL Operations
To reduce boilerplate and optimize for performance the Neo4j GraphQL Library automatically generates a single database query for any arbitrary GraphQL request. This means the developer does not need to implement resolvers and each GraphQL operation results in a single roundtrip to the database.
Extend GraphQL With Cypher
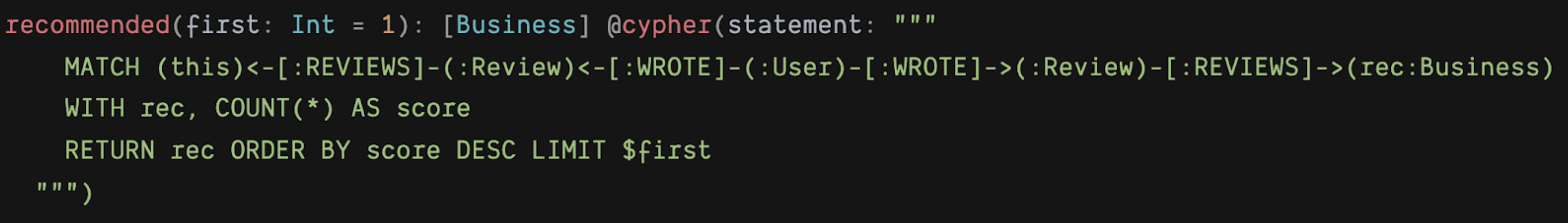
To add custom logic beyond CRUD operations, you can use the @cypher GraphQL schema directive to add computed fields bound to a Cypher query to the GraphQL schema.
Neo4j GraphQL Library Quickstart
The focus of this course is using the Neo4j GraphQL Library to build GraphQL APIs backed by the Neo4j graph database. Each lesson will be a hands-on mix of introducing concepts, examples, exercises, and quizzes.
| As mentioned previously you won’t be installing or running the Neo4j GraphQL Library locally, instead you will use Codesandbox to run the code. In this course you will be using a Codesandbox environment and won’t need to worry about performing these quickstart steps. |
However, it’s important to understand how to install and get started with the Neo4j GraphQL Library after you have completed this course.
The Neo4j GraphQL Library can be installed using npm as shown here:
$ npm install @neo4j/graphql graphql neo4j-driver apollo-serverThe Neo4j GraphQL Library is a Node.js JavaScript library that can be used with JavaScript GraphQL implementations.
// index.js
const { Neo4jGraphQL } = require("@neo4j/graphql");
const neo4j = require("neo4j-driver");
const { ApolloServer } = require("apollo-server");
const typeDefs = `
type Movie {
title: String
year: Int
imdbRating: Float
genres: [Genre] @relationship(type: "IN_GENRE", direction: OUT)
}
type Genre {
name: String
movies: [Movie] @relationship(type: "IN_GENRE", direction: IN)
}
`;
const driver = neo4j.driver(
"bolt://localhost:7687",
neo4j.auth.basic("neo4j", "letmein")
);
const neoSchema = new Neo4jGraphQL({ typeDefs, driver });
const server = new ApolloServer({
schema: neoSchema.schema,
context: ({ req }) => ({ req }),
});
server.listen(4000).then(() => console.log("Online"));Then to start a local GraphQL API:
node index.jsThis will start a local GraphQL API and will also serve the GraphQL Playground IDE for querying the API or exploring documentation using GraphQL’s introspection feature.
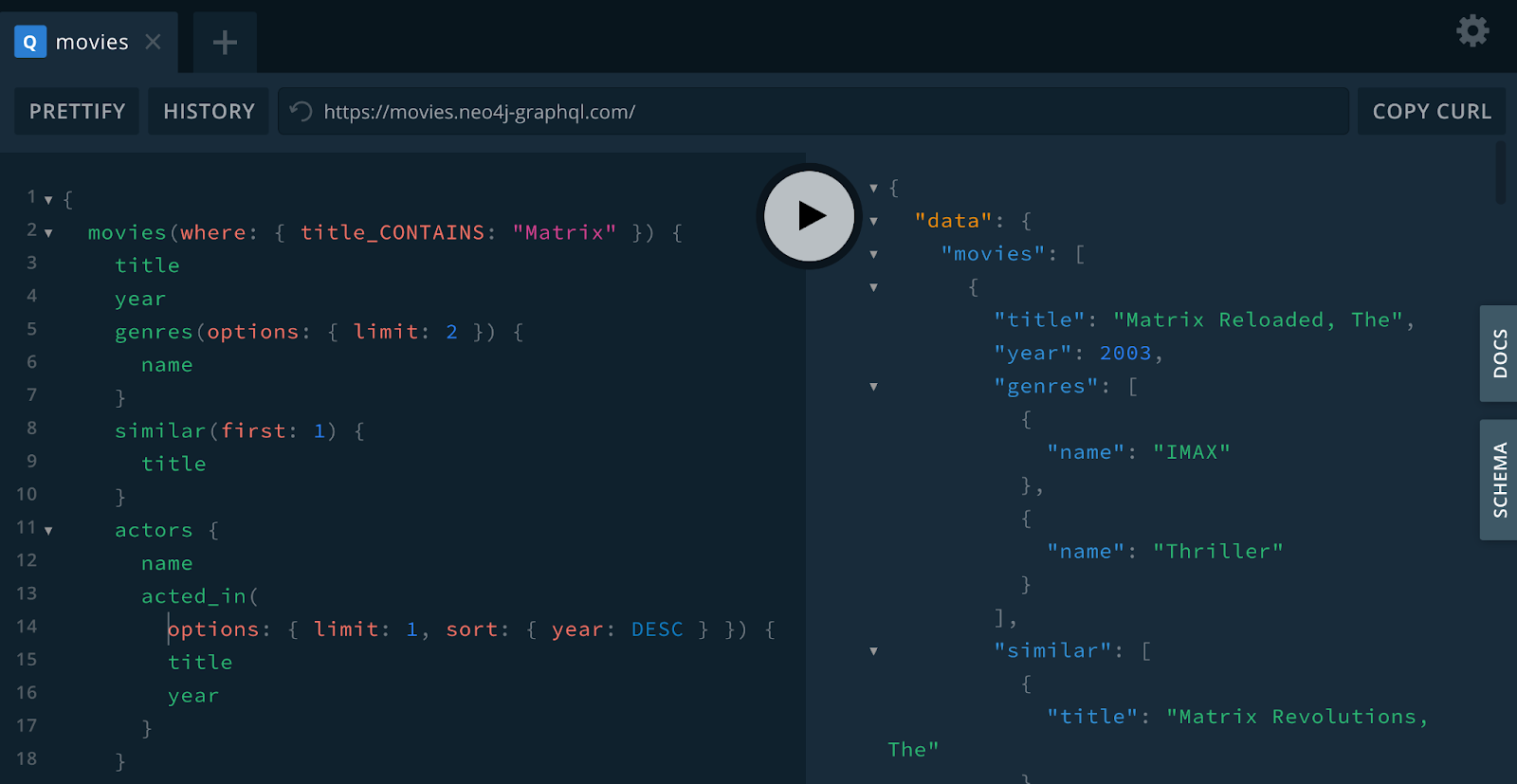
Exercise: Exploring The Movies GraphQL API
-
To familiarize yourself with GraphQL and writing GraphQL queries, open the public movies GraphQL API at movies.neo4j-graphql.com.
-
Explore GraphQL Playground by executing the following queries, and opening the Docs and Schema tab to see the type definitions.
-
Modify the queries by adding additional fields in the selection set and see how the results change.
{
movies(options: { limit: 10 }) {
title
actors {
name
}
}
}{
directors(where: {name:"Robert Redford"}) {
name
directed {
title
plot
}
}
}The GraphQL Playground embed above is interactive and can be used directly in this page or if you’d like some more screen real estate can be opened in a new tab at movies.neo4j-graphql.com
Check Your Understanding
Question 1
The n+1 query problem is a common problem developers face when building GraphQL APIs and can lead to poor performance if not properly addressed.
Is this statement true or false?
-
True
-
False
Summary
In this lesson, we introduced GraphQL and the features of the Neo4j GraphQL Library. In the next lesson we get started using the Neo4j GraphQL Library to build a GraphQL API backed by Neo4j.
Need help? Ask in the Neo4j Community