Supply Chain Intelligence: Future-Proof Your Supply Network

Senior Director of Global Solutions, Neo4j
5 min read
Supply chain intelligence is a systematic approach to collecting, analyzing, and acting on data to improve performance across all aspects of the supply chain. With supply chain intelligence, companies acquire real-time information that strengthens business decision-making and operational efficiency.
A key benefit of using supply chain intelligence is improved risk management — comprehensive, real-time supply chain data allows companies to identify and mitigate risks and rapidly respond to crises. Other benefits include faster time to market, better customer service, and cost control via improved forecasting and operational efficiency.
As companies explore new avenues for increased competitiveness and profitability in an uncertain business climate, adopting a data-driven approach to supply chain management has quickly become a key differentiator.
Challenges for Modern Supply Chains — and Supply Chain Intelligence
Supply chain intelligence is particularly critical today. Modern supply chains are incredibly complex, comprising factories, warehouses, labor resources, and transportation routes and modes, among other elements. And they’re more geographically extensive than ever, often spanning oceans and continents.
That scope and complexity have introduced a host of new vulnerabilities: border disputes, epidemics, natural disasters, retaliatory trade policies, and more.
Supply chain leaders also have to contend with rapid shifts in consumer demand and growing calls for transparency driven by concerns about sustainability and ethical sourcing.
In response, they’ve begun to rethink their priorities. Increasingly, they’re focusing on:
-
- End-to-end visibility. Can you track goods in transit across the entire supply chain with a granular understanding of activity and inventory? Does your strategy combine AI and machine learning to facilitate horizontal integration across functions?
- Forecasting. Can you accurately predict disruptions and their ripple effects? Reliable forecasting requires analysis of complex supply chain relationships to reveal hidden bottlenecks.
- Real-time decision-making. Can you harness a sea of disparate supply chain data and immediately identify patterns within it?
- Cost control. Do you employ holistic cost-control analytics, including root-cause analysis? Are you targeting structural savings across the entire supply network to enable sustainable cost control?
- Sustainability. How do you measure social and environmental impact? You might need to correlate metadata with products and inventories, track your carbon footprint, or audit delivery facilities.
To achieve these objectives, supply chain leaders are turning to supply chain intelligence — and the data technologies that make it possible.
How to Apply a Supply Chain Technology Strategy
Because modern supply chains are vast and complex, effective supply chain management depends on a deep understanding of the relationships between their components: distribution pathways, products, suppliers, etc. But data on those components comes from many sources and takes many forms. Identifying the right tools to analyze large volumes of interconnected data is a key strategic activity to ensure the resilience of your supply chain over the long term.
If your organization relies on spreadsheets or relational databases, it’s exceptionally time-consuming to map out interconnected, unstructured data from different sources. Relational databases model data relationships inefficiently, and become clunky when used to manage the kinds of datasets involved in supply chain management.
Graph databases, on the other hand, have become the leading technology for supply chain management because they excel at modeling complex relationships. Relationships are first-class entities in a graph structure, so you can easily model the elements of your supply chain as data points and map out the explicit relationships between them. That makes it possible for algorithms to rapidly traverse the paths of your supply chain and extract insights — allowing you to respond to disruptions instantly.
If you need to head off a crisis by rerouting a shipment or finding a shorter route to a distribution center, for example, you can do it in real time. Since graph databases are built to handle relationships between data, performance will remain consistent even as your data volumes grow.
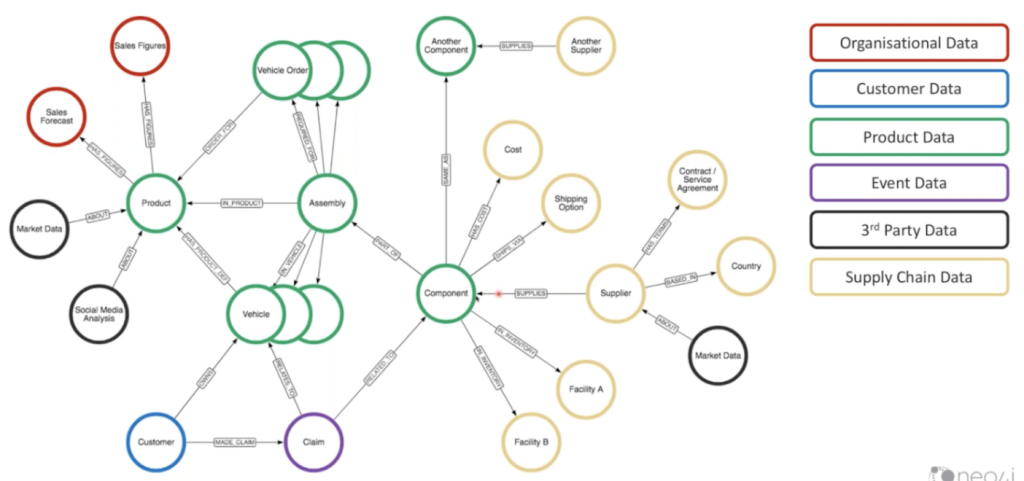
You can also add new types of data without jeopardizing performance. Graph databases don’t have rigid schemas, so it’s easy to add data classes and entities when you introduce new products or product categories. Accommodating new suppliers and channel partners is similarly easy — no need to refactor applications or the data platform.
Supply Chain Intelligence in the Real World
Procurement services firm Scoutbee is a good example of how supply chain intelligence operates in the real world. By leveraging the database and analytics capabilities of Neo4j, Scoutbee enables companies like Unilever, Siemens, and Audi to visualize supplier interdependencies and optimize partnerships in real time.
“We offer 360-degree supplier views — we’re not just looking at a supplier from one data perspective, but bringing in all the data we have on a supplier and revealing the entire spectrum of relationships between them,” says Nischal Padmanabha, VP of Data and ML at Scoutbee.
Supplier discovery isn’t just more powerful with Neo4j, it’s also 75 percent faster and 85 percent less labor-intensive. Instead of spending 100–180 working hours over 24 weeks, Scoutbee clients now spend 8–12 hours over six weeks.
Graph Technology Optimizes the Entire Supply Chain
In its most recent supply chain strategy report, Gartner encourages supply chain leaders to adopt a more holistic, data-driven management approach. Graph databases, with their ability to handle complexity, large datasets, and intricate relationships, allow organizations to do just that — to visualize the supply chain from end to end and optimize it in an intelligent, integrated way.
If you’re interested in learning more about the impact of graph databases on supply chain management, take a look at our new white paper, How Graph Technology Drives Modern Supply Chain Strategy — a deep dive into graph capabilities and how they support supply chain intelligence and modernization. You’ll learn how graph databases make it easy to model recursive relationships, for example, and how graph algorithms can help you anticipate bullwhip effects, pinpoint potential bottlenecks, and prepare for disruptions.
The paper focuses on:
-
- The unprecedented challenges facing modern supply chains
- Why supply chains cannot be modernized on legacy systems
- The technical capabilities of graph databases and analytics in a supply chain context
- Real-world examples of supply chain transformation in the military, automotive, and procurement sectors
It’s essential reading for anyone looking to build a future-proof supply chain.