Triggers
Triggers allow the registration of Cypher queries that are called when data in Neo4j is changed (created, updated, deleted). You can run them before or after commit.
|
All these
Moreover, they accept as first parameter the name of the database towards which we want to install/update/remove the triggers. Through this implementation, we can use these procedures in a cluster environment, by leveraging the cluster routing mechanism. These procedures are only executable by a user with admin permissions.
If this is not the case, the procedure throws an exception with the message |
|
Installing, updating or removing a trigger is an eventually consistent operation.
Therefore, they are not immediately added/updated/removed,
but they have a refresh rate handled by the Apoc configuration |
By default triggers are disabled.
We can enable them by setting the following property in apoc.conf:
apoc.trigger.enabled=true
apoc.trigger.refresh=60000| Option Key | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
apoc.trigger.enabled |
true/false, default false |
Enable/Disable the feature |
apoc.trigger.refresh |
number, default 60000 |
Interval in ms after which a replication check is triggered across all cluster nodes |
| Qualified Name | Type | Release |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The transaction data from Neo4j is turned into appropriate data structures to be consumed as parameters to your statement, i.e. $createdNodes.
The parameters available are:
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
transactionId |
returns the id of the transaction. Note that this value only works with the 'after' and 'afterAsync' phases (see the Trigger Phase Table).
Otherwise, it has the value |
commitTime |
return the date of the transaction in milliseconds |
createdNodes |
when a node is created our trigger fires (list of nodes) |
createdRelationships |
when a relationship is created our trigger fires (list of relationships) |
deletedNodes |
when a node is deleted our trigger fires (list of nodes) |
deletedRelationships |
when a relationship is deleted our trigger fires (list of relationships) |
removedLabels |
when a label is removed our trigger fires (map of label to list of nodes) |
removedNodeProperties |
when a properties of node is removed our trigger fires (map of key to list of map of key,old,node) |
removedRelationshipProperties |
when a properties of relationship is removed our trigger fires (map of key to list of map of key,old,relationship) |
assignedLabels |
when a labes is assigned our trigger fires (map of label to list of nodes) |
assignedNodeProperties |
when node property is assigned our trigger fires (map of key to list of map of key,old,new,node) |
assignedRelationshipProperties |
when relationship property is assigned our trigger fires (map of key to list of map of key,old,new,relationship) |
metaData |
a map containing the metadata of that transaction. Transaction meta data can be set on client side e.g. via https://neo4j.com/docs/api/java-driver/current/org/neo4j/driver/TransactionConfig.html#metadata-- |
You can use these helper functions to extract nodes or relationships by label/relationship-type or updated property key.
| Qualified Name | Type | Release |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The 3rd parameter of the apoc.trigger.install() is a map {phase: PHASE}, where PHASE is a string which can have one of the following values:
|
Description |
|
The trigger will be activate right |
|
The trigger will be activate right after the |
|
The trigger will be activate right |
|
The trigger will be activate right |
Triggers Examples
We could add a trigger that when is added a specific property on a node, that property is added to all the nodes connected to this node
Dataset (in default database 'neo4j')
CREATE (d:Person {name:'Daniel', surname: 'Craig'})
CREATE (l:Person {name:'Mary', age: 47})
CREATE (t:Person {name:'Tom'})
CREATE (j:Person {name:'John'})
CREATE (m:Person {name:'Michael'})
CREATE (a:Person {name:'Anne'})
CREATE (l)-[:DAUGHTER_OF]->(d)
CREATE (t)-[:SON_OF]->(d)
CREATE (t)-[:BROTHER]->(j)
CREATE (a)-[:WIFE_OF]->(d)
CREATE (d)-[:SON_OF]->(m)
CREATE (j)-[:SON_OF]->(d)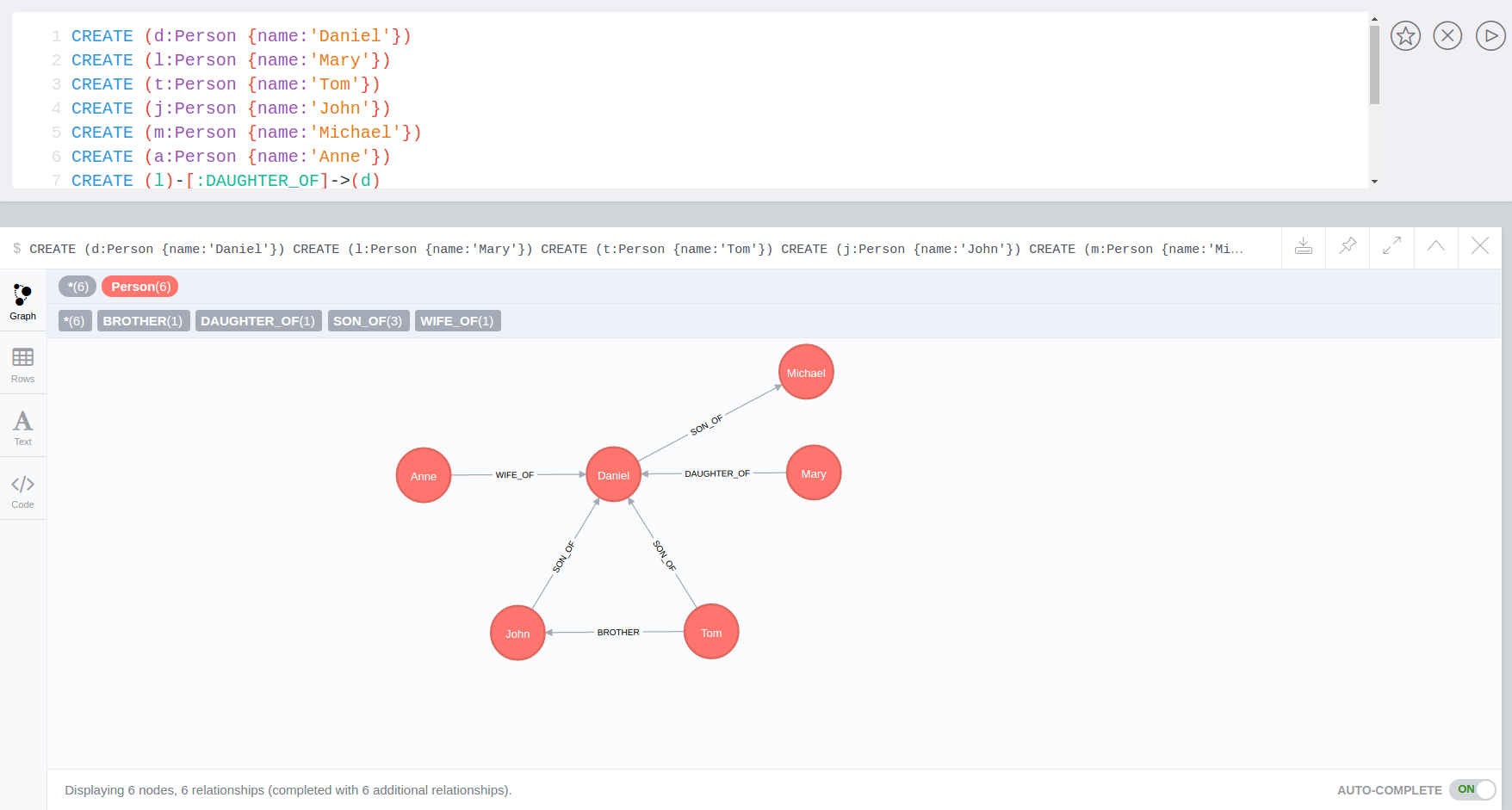
With the above dataset, if we add a trigger and we execute for example, MATCH (n:Person) WHERE n.name IN ['Daniel', 'Mary'] SET n.age=55, n.surname='Quinn',
the $assignedNodeProperties which can be used in the trigger statement,
will be as follows (where NODE(1) is (:Person {name: 'Daniel'}), and NODE(2) is (:Person {name: 'Mary'})):
{
age: [{
node : NODE(1),
new: 55,
old: null,
key: "age"
},
{
node: NODE(2),
new: 55,
old: 47,
key: "age"
}],
surname: [{
node: NODE(1),
new: "Quinn",
old: "Craig",
key: "surname"
},
{
node: NODE(2),
new: "Quinn",
old: null,
key: "surname"
}]
}As we can see, the result is a map of list, where the keys are the assigned properties, and the values are a list of entities involved.
Every element of a list have the node itself, the new value of the changed properties, the old value (or null if the property didn’t exist) and the key with the property name.
The $removedNodeProperties parameter has the same structure and logic (of course, in this case new values will be always null).
Same thing regarding assignedRelationshipProperties and removedRelationshipProperties,
with the only difference that instead of node: NODE(n) key, we’ll have relationship: RELATIONSHIP(n).
For example, if we want to create a trigger that at every SET, updates 2 properties time and lasts
with the current date and the property updated, we can do:
CALL apoc.trigger.install('neo4j', 'setLastUpdate',
"UNWIND keys($assignedNodeProperties) AS k
UNWIND $assignedNodeProperties[k] AS map
WITH map.node AS node, collect(map.key) AS propList
MATCH (n)
WHERE id(n) = id(node) AND NOT 'lasts' in propList // to prevent loops
SET n.time = date(), n.lasts = propList",
{phase: 'afterAsync'});Note that the apoc.trigger.install, as well as the apoc.trigger.drop, apoc.trigger.dropAll, apoc.trigger.stop and apoc.trigger.start,
have to be executed in the system database
In the example above, we put match (n) where id(n) = id(node) to demonstrate that the we pull the node by id into parameters.
Anyway, we can get rid of this one and change last row with SET node.time = date(), node.lasts = propList.
Note that we have to add the condition AND NOT 'lasts' IN propList to prevent an infinite loop as this SET will trigger this query again.
Then, after a time defined by the configuration apoc.trigger.refresh, we can execute:
MATCH (n:Person {name: 'Daniel'}) set n.age = 123, n.country = 'Italy'Executing
MATCH (n:Person {name: 'Daniel'}) return nwe can see the property time with the today’s date, and lasts=['country','age'].
So when we add the surname property on a node, it’s added to all the nodes connected (in this case one level deep)
MATCH (d:Person {name:'Daniel'})
SET d.surname = 'William'Now we add the trigger using apoc.trigger.propertiesByKey on the surname property
CALL apoc.trigger.install('neo4j', 'setAllConnectedNodes','UNWIND apoc.trigger.propertiesByKey($assignedNodeProperties,"surname") as prop
WITH prop.node as n
MATCH(n)-[]-(a)
SET a.surname = n.surname', {phase:'after'});So when we add the surname property on a node, it’s added to all the nodes connected (in this case one level deep)
MATCH (d:Person {name:'Daniel'})
SET d.surname = 'William'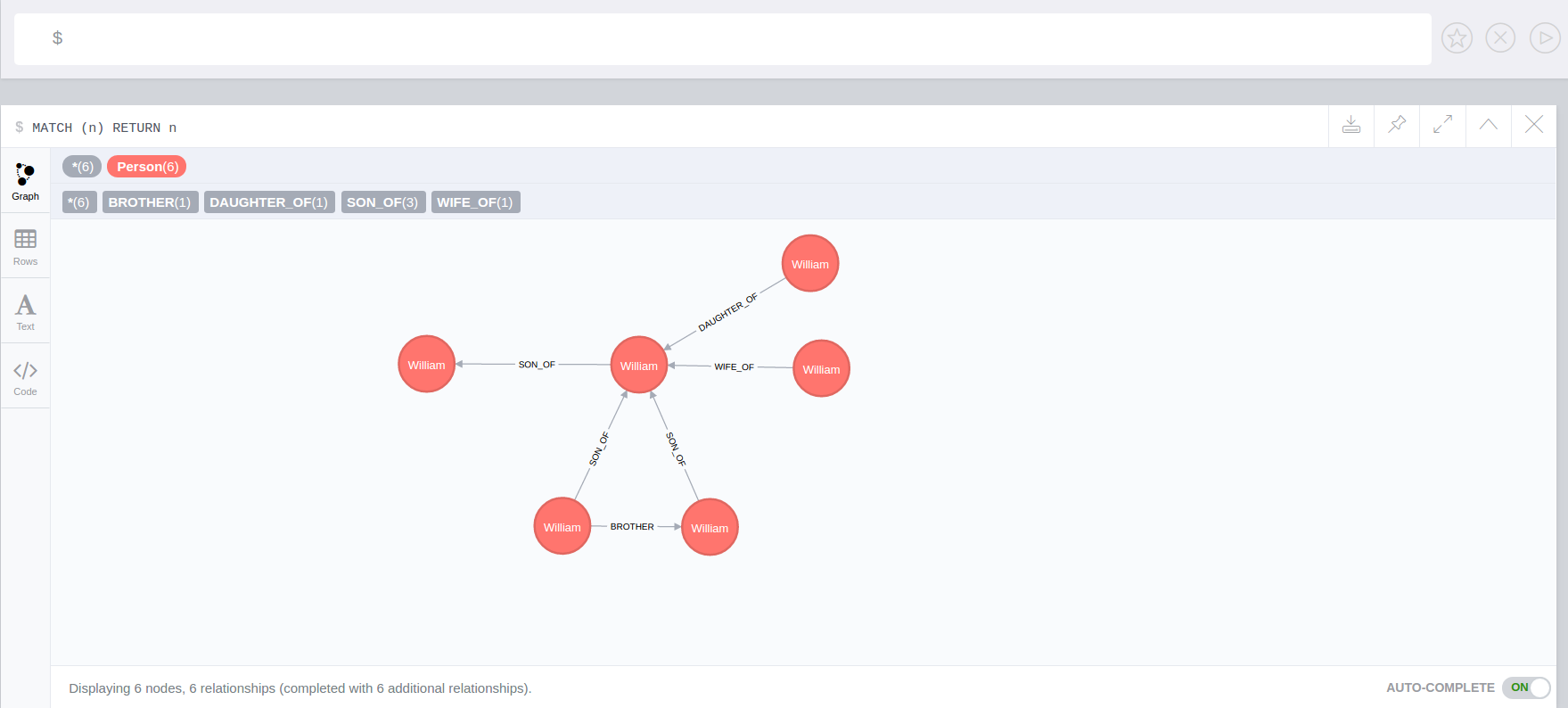
The surname property is add/change on all related nodes
Dataset (in a database 'dbTest')
CREATE (k:Actor {name:'Keanu Reeves'})
CREATE (l:Actor {name:'Laurence Fishburne'})
CREATE (c:Actor {name:'Carrie-Anne Moss'})
CREATE (m:Movie {title:'Matrix'})
CREATE (k)-[:ACT_IN]->(m)
CREATE (l)-[:ACT_IN]->(m)
CREATE (c)-[:ACT_IN]->(m)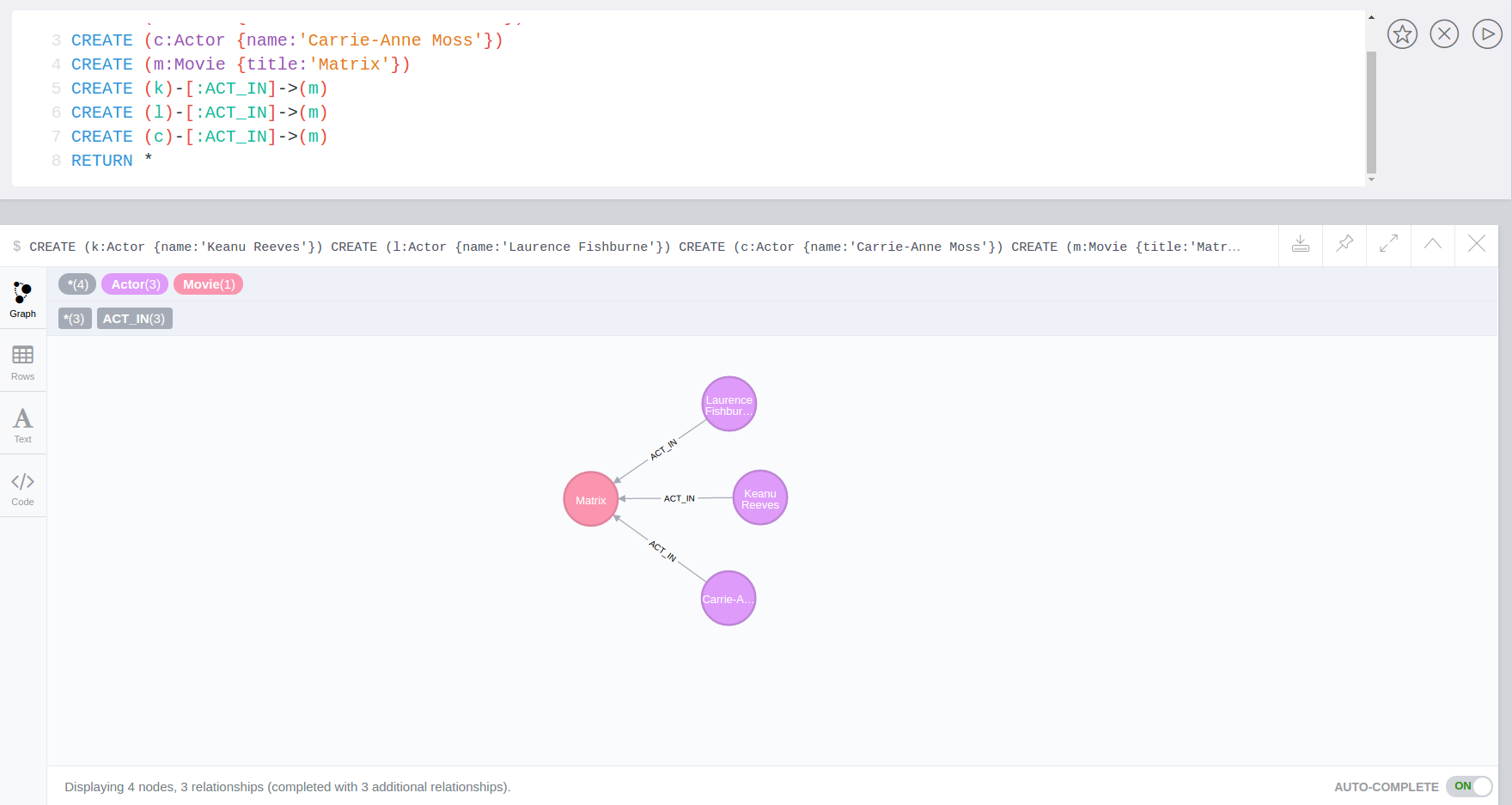
We add a trigger using apoc.trigger.nodesByLabel that when the label Actor of a node is removed, update all labels Actor with Person
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', 'updateLabels',"UNWIND apoc.trigger.nodesByLabel($removedLabels,'Actor') AS node
MATCH (n:Actor)
REMOVE n:Actor SET n:Person SET node:Person", {phase:'before'})MATCH(k:Actor {name:'Keanu Reeves'})
REMOVE k:Actor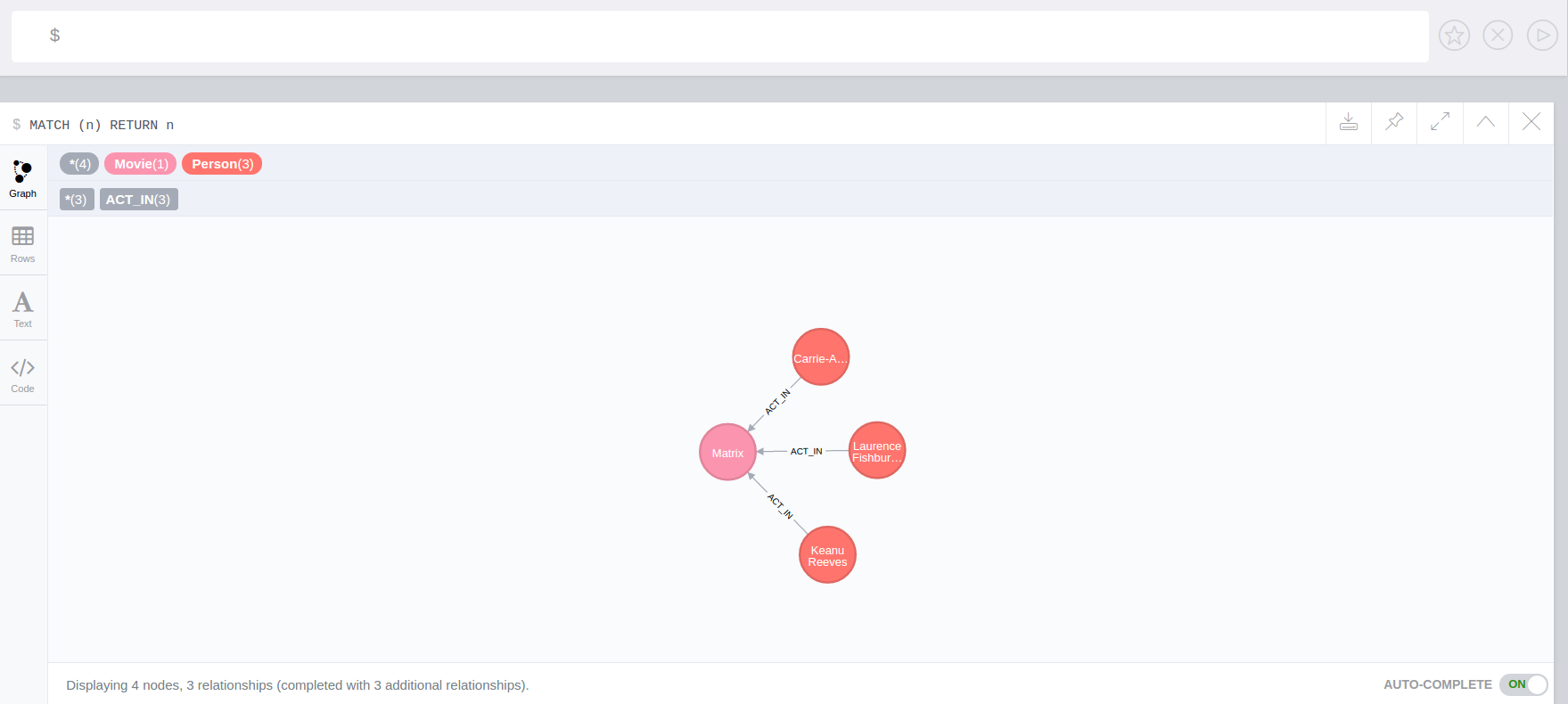
We can add a trigger that connect every new node with label Actor and as name property a specific value
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', 'create-rel-new-node',"UNWIND $createdNodes AS n
MATCH (m:Movie {title:'Matrix'})
WHERE n:Actor AND n.name IN ['Keanu Reeves','Laurence Fishburne','Carrie-Anne Moss']
CREATE (n)-[:ACT_IN]->(m)", {phase:'before'})CREATE (k:Actor {name:'Keanu Reeves'})
CREATE (l:Actor {name:'Laurence Fishburne'})
CREATE (c:Actor {name:'Carrie-Anne Moss'})
CREATE (a:Actor {name:'Tom Hanks'})
CREATE (m:Movie {title:'Matrix'})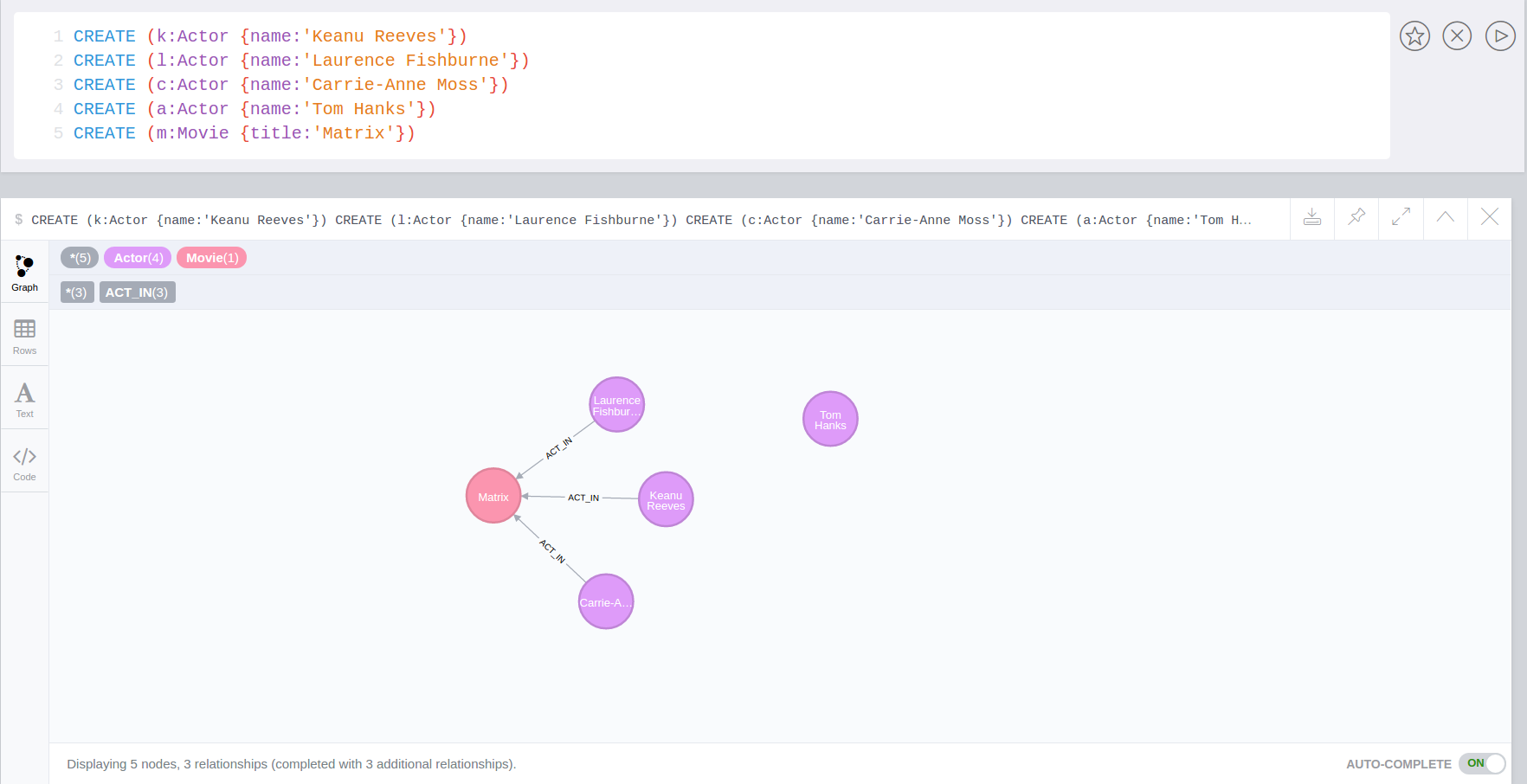
Generally, is recommended to use afterAsync phase, to prevent some annoying transaction locks.
For example, given this trigger:
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', 'lockTriggerTest1','UNWIND apoc.trigger.propertiesByKey($assignedNodeProperties,"name") as prop
WITH prop.node as n
CREATE (z:AnotherNode {myId: id(n)})
CREATE (n)-[:GENERATED]->(z)',
{phase:'after'});if we execute:
MATCH (n:Person {name: 'John'}) set n.name = 'Jack'the query will remain pending indefinitely.
To solve this, we can use {phase:'afterAsync'}
We have the possibility of pausing a trigger without removing it, in case we might need it in the future.
Note that this procedure and the apoc.trigger.start ones are eventually consistent,
so we need to wait some amount of time for the changes to propagate. This amount of time is defined by the configuration apoc.trigger.refresh.
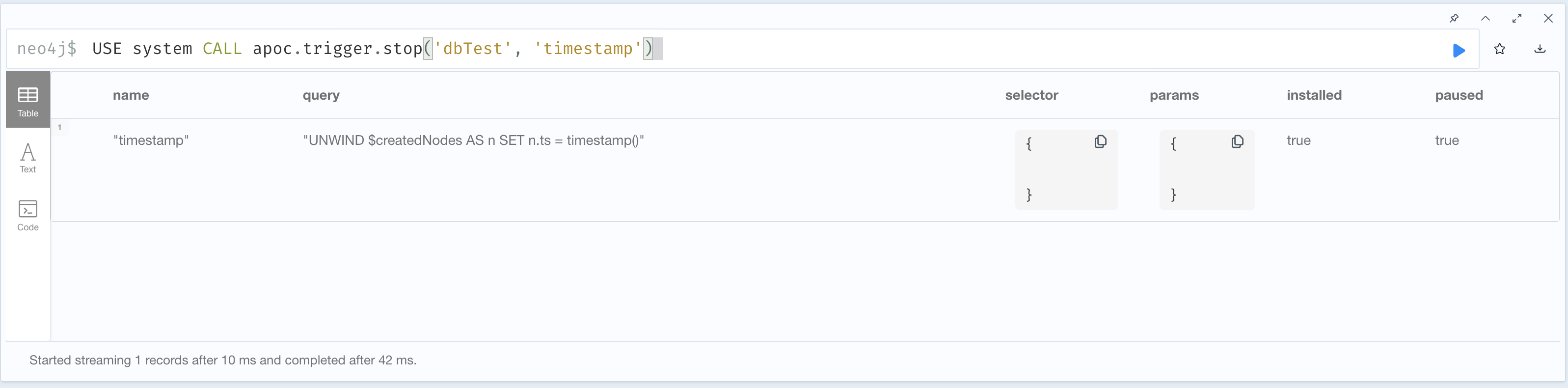
When you need again of a trigger paused
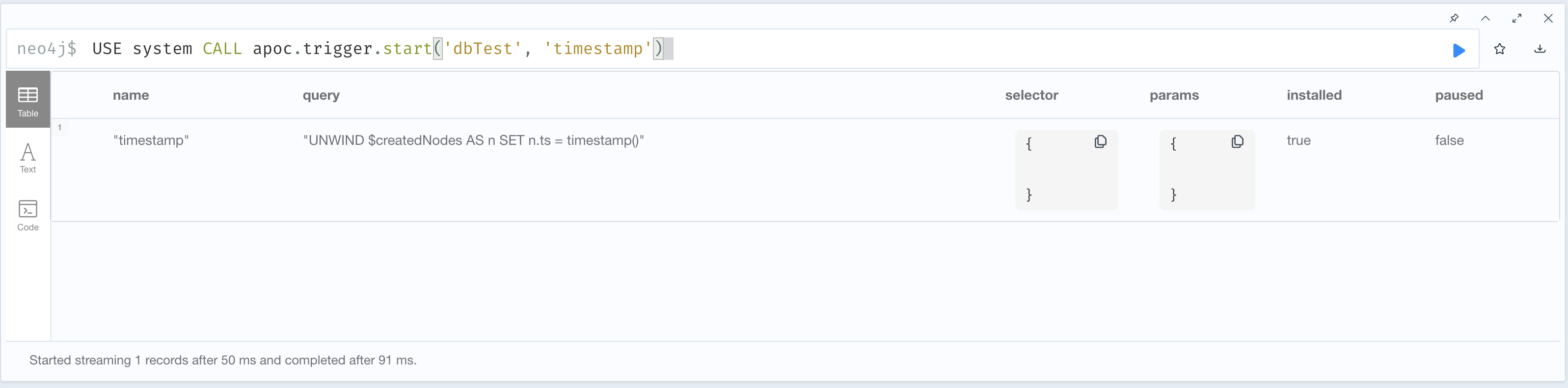
For this example, we would like that all the reference node properties are of type STRING
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', "forceStringType",
"UNWIND apoc.trigger.propertiesByKey($assignedNodeProperties, 'reference') AS prop
CALL apoc.util.validate(apoc.meta.type(prop) <> 'STRING', 'expected string property type, got %s', [apoc.meta.type(prop)]) RETURN null", {phase:'before'})CREATE (a:Node) SET a.reference = 1
Neo.ClientError.Transaction.TransactionHookFailedWe can pass as a 4th parameter, a {params: {parameterMaps}} to insert additional parameters.
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', 'timeParams','UNWIND $createdNodes AS n SET n.time = $time', {}, {params: {time: timestamp()}});If we to create a 'before' or 'after' trigger query, with $deletedRelationships or $deletedNodes,
and then we want to retrieve entities information like labels and/or properties,
we cannot use the 'classic' cypher functions labels() and properties(),
but we can leverage on virtual nodes and relationships,
via the functions apoc.trigger.toNode(node, $removedLabels, $removedNodeProperties) and apoc.trigger.toRelationship(rel, $removedRelationshipProperties).
So that, we can retrieve information about nodes and relations,
using the apoc.any.properties, and the apoc.node.labels functions.
For example, if we want to create a new node with the same properties (plus the id) and with an additional label retrieved for each deleted node, we can execute:
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', 'myTrigger',
"UNWIND $deletedNodes as deletedNode
WITH apoc.trigger.toNode(deletedNode, $removedLabels, $removedNodeProperties) AS deletedNode
CREATE (r:Report {id: id(deletedNode)}) WITH r, deletedNode
CALL apoc.create.addLabels(r, apoc.node.labels(deletedNode)) yield node with node, deletedNode
set node+=apoc.any.properties(deletedNode)" ,
{phase:'before'})Or also, if we want to create a node Report with the same properties (plus the id and rel-type as additional properties) for each deleted relationship, we can execute:
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', 'myTrigger',
"UNWIND $deletedRelationships as deletedRel
WITH apoc.trigger.toRelationship(deletedRel, $removedRelationshipProperties) AS deletedRel
CREATE (r:Report {id: id(deletedRel), type: apoc.rel.type(deletedRel)})
WITH r, deletedRelset r+=apoc.any.properties(deletedRel)" ,
{phase:'before'})|
By using phase 'afterAsync', we don’t need to execute |
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', 'timestamp','UNWIND $createdNodes AS n SET n.ts = timestamp()', {});
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', 'lowercase','UNWIND $createdNodes AS n SET n.id = toLower(n.name)', {});
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', 'txInfo', 'UNWIND $createdNodes AS n SET n.txId = $transactionId, n.txTime = $commitTime', {phase:'after'});
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', 'count-removed-rels','MATCH (c:Counter) SET c.count = c.count + size([r IN $deletedRelationships WHERE type(r) = "X"])', {})
CALL apoc.trigger.install('dbTest', 'lowercase-by-label','UNWIND apoc.trigger.nodesByLabel($assignedLabels,"Person") AS n SET n.id = toLower(n.name)', {})Remove triggers
If we want to remove the trigger with name 'test' in 'neo4j' database, we can run the following query:
CALL apoc.trigger.drop('neo4j', 'test')If we want to remove all triggers in 'neo4j' db, we can execute
CALL apoc.trigger.dropAll('neo4j')List of triggers
If we want to get the list of triggers, for example if we have one trigger created via:
CALL apoc.trigger.install('neo4j', 'count-removals',
'MATCH (c:Counter) SET c.count = c.count + size([f IN $deletedNodes WHERE id(f) > 0])',
{})we can execute (also in this case, after a time defined by the configuration apoc.trigger.refresh):
CALL apoc.trigger.show('neo4j')| name | query | selector | params | installed | paused |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
"count-removals" |
{} |
{} |
TRUE |
FALSE |
|
Please note that, since the trigger operations are eventually consistent (based on If you want the list of currently installed triggers, you can use the apoc.trigger.list against the session database ("neo4j" in the above case) |
Export metadata
|
To import triggers in another database (for example after a |