Manually registered agent
Agent registration is the process of manually acquiring token information from NOM UI to allow the agent to communicate with NOM server.
This step can be omitted by using agent self-registration as described in Self-registering agent.
Register agent
Before installing an agent, it needs to be registered with the NOM server to provide server communication configuration.
-
Click the top right settings icon that redirects you to the global settings.
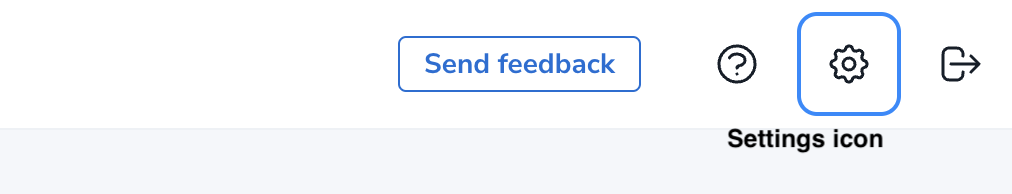
-
Click Agents, where you will see a list of all registered agents along with their last contact times and versions.
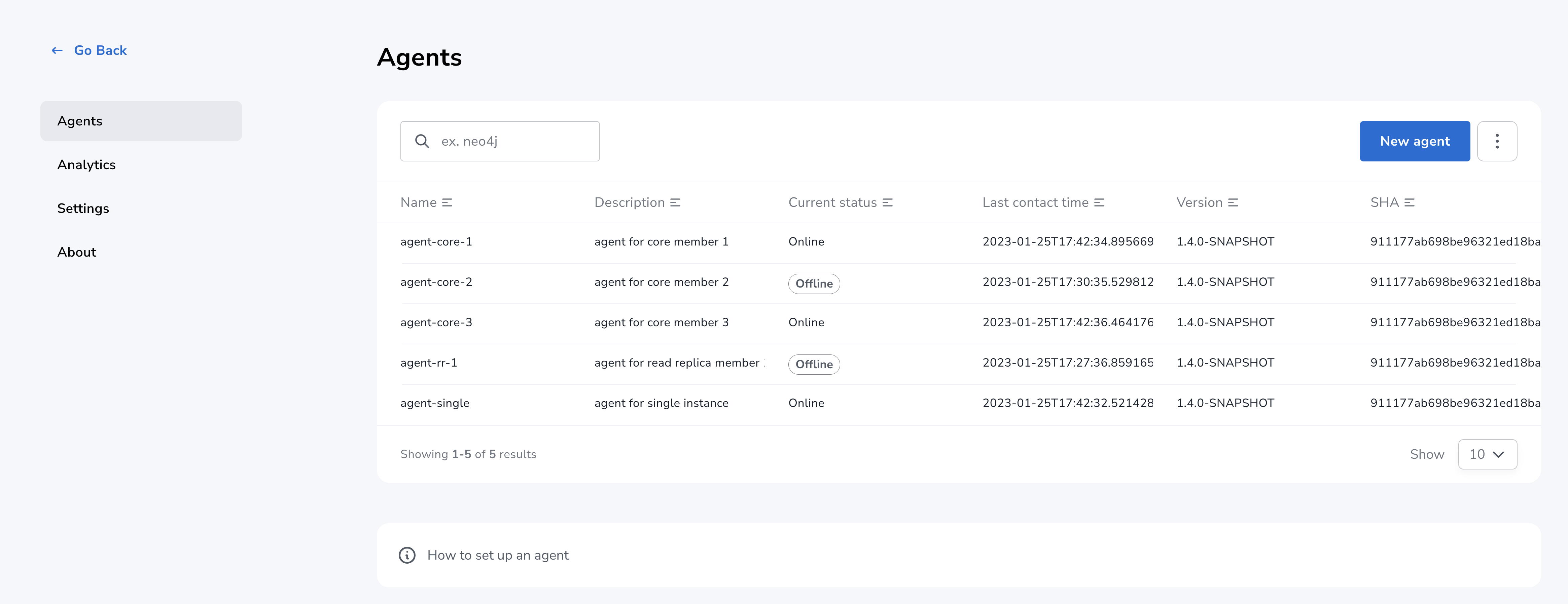
-
Click Register New Agent button, and enter the name and description for your new agent followed by clicking Register button.
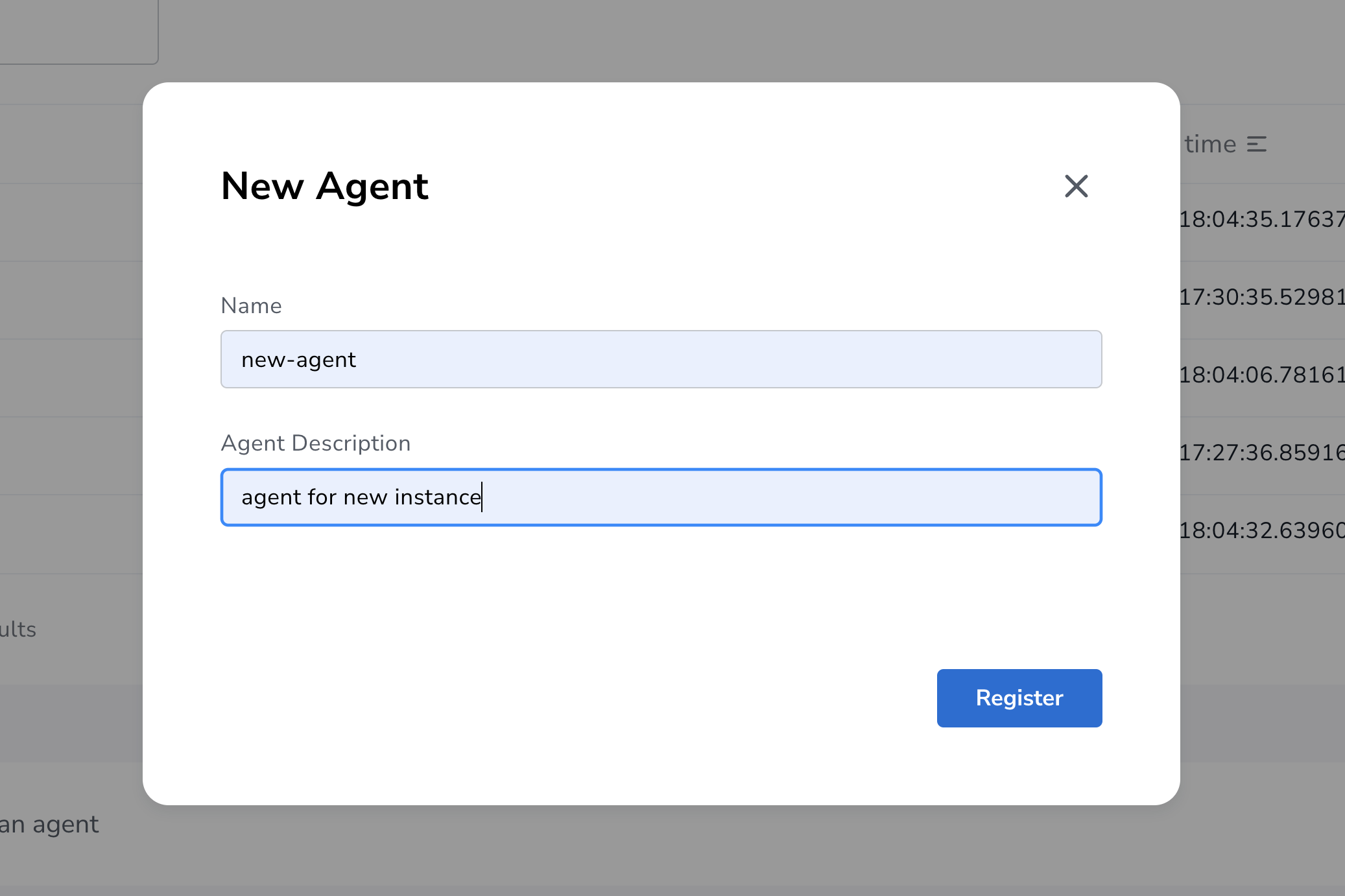
-
The agent will be created and randomly generated agent credentials will be displayed on the screen.
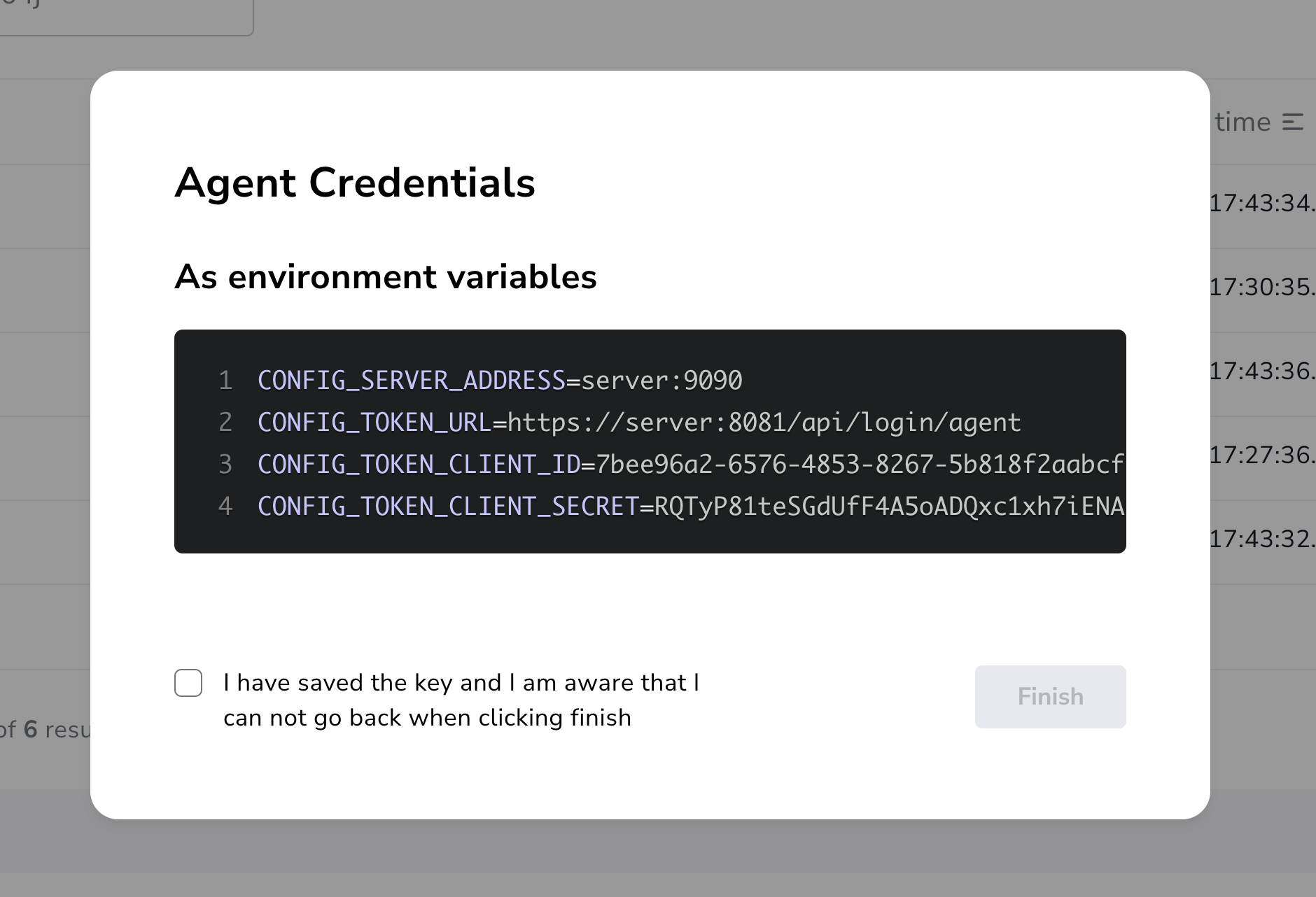
The credentials and other key agent configuration values are displayed as environment variable declarations. You can copy them over to the host for ease of agent configuration.
-
After you have captured the credentials, click the confirmation checkbox and Finish button. Newly created agent will be displayed on the list of agents.
Running as a service
To run an agent in service mode means that the agent process runs in the background and monitors the instance. The agent lifecycle is handled by the operating system service manager. Best practice is to run an agent in service mode.
Linux (systemd)
Setting arguments
Run the following to edit the service:
systemctl edit neo4j-ops-manager-agent.serviceSet environment variables by either setting Environment or EnvironmentFile options. For example, using the Environment options, the override file can look like this:
[Service]
Environment="CONFIG_SERVER_ADDRESS=<server grpc address>"
Environment="CONFIG_TOKEN_URL=<server http login url>"
Environment="CONFIG_TOKEN_CLIENT_ID=<client id>"
Environment="CONFIG_TOKEN_CLIENT_SECRET=<client secret>"
Environment="CONFIG_TLS_TRUSTED_CERTS=</path/to/trusted/certs/pem/file>"
Environment="CONFIG_LOG_FILE=</path/to/nom-agent/log.txt>"
Environment="CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_NAME=<instance name>"
Environment="CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_BOLT_URI=<bolt uri of the local instance>"
Environment="CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_BOLT_USERNAME=<local instance user name>"
Environment="CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_BOLT_PASSWORD=<local instance password>"
Environment="CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_QUERY_LOG_PORT=<an available port>"
Environment="CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_LOG_CONFIG_PATH=<path to server-logs.xml>"Please refer to the full list of options here.
Windows
Setting arguments
-
Open registry editor and navigate to
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\neo4j-ops-manager-agent. -
Create a key of type
REG_MULTI_SZnamedEnvironmentand add your environment variables, each on a separate line, for example:CONFIG_SERVER_ADDRESS=<server grpc address> CONFIG_TOKEN_URL=<server http login url> CONFIG_TOKEN_CLIENT_ID=<client id> CONFIG_TOKEN_CLIENT_SECRET=<client secret> CONFIG_TLS_TRUSTED_CERTS=</path/to/the/trusted/certs/pem> CONFIG_LOG_FILE=</path/to/nom-agent/log.txt> CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_NAME=<instance name> CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_BOLT_URI=<bolt uri of the local instance> CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_BOLT_USERNAME=<local instance user name> CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_BOLT_PASSWORD=<local instance password> CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_QUERY_LOG_PORT=<an available port> CONFIG_INSTANCE_1_LOG_CONFIG_PATH=<path to server-logs.xml>
Please refer to the full list of options here.
Running as a console application
All configuration values for the agent should be set as environment variables before starting the agent.
agent consoleVerify agent setup
Ensure agent has contacted NOM server, is online and is reporting DBMS(s) correctly.
-
Return to Agents listing in global settings

-
Identify the newly created agent.
-
Check that there is a value for Last contact time.
-
If the agent has never contacted NOM server then go back to where the agent is running and check the logs. It may be that the server address is configured incorrectly or the TLS certificates are not correctly specified.
-
-
Verify that the agent has a current status of
Online.-
If the agent is not currently online then go to where it is running and check the logs.
-
-
Hover over the newly added agent and select "View Configuration" from the menu on the right to show agent configuration. Check configuration is as expected.
-
Navigate to the home page (if this agent is the first to manage an instance in a DBMS, it may take a few minutes for the DBMS to appear).
-
Select the Alerts tab and make sure that there are no alerts for any of the DBMSs managed by the new agent.
Agent configuration reference
The tables here list configuration keys and values to be set for them.
Server communication configuration (manually registered agent)
The following environment variables need to be set to allow the agent to communicate with the NOM Server.
Copy the first four from the Agent Credentials dialog in the register step.
| Variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Server GRPC Address |
server:9090 |
|
Server Token URL |
https://server:8080/api/login/agent |
|
Client ID for the agent |
` 3ff98478-d6d2-4e1b-b816-e758c835f076` |
|
Client secret for the agent |
secret |
|
PEM encoded trusted CA list () |
|
|
Since agent-server communication needs to be encrypted, you need to configure the agent so that it trusts the server’s certificates.
The file that contains the trusted certificate list (PEM encoded) can be specified through the |
Agent logging configuration
The following environment variables specify log configuration for the agent:
| Variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Log level (debug,info,warn,error) |
info |
|
Path to the log file |
|
Monitored instance configuration
The following environment variables need to be set to allow the agent to access the instance.
|
If there is more than one DBMS being monitored by the same agent, repeat and enumerate the configuration of each DBMS by replacing the digit |
| Variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Name of first instance |
my-instance-1 |
|
Bolt URI for first instance with bolt or bolt+s protocol |
bolt://localhost:7687 or bolt+s://localhost:7687 or bolt+ssc://localhost:7687, depending on the local database setup |
|
Bolt username for first instance |
neo4j |
|
Bolt password for first instance |
password |
|
The instance name that you specify for |
Query log collection configuration
| Variable | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Port for connecting the agent to the Neo4j log4j appender. If not set, the query log collection feature is treated as disabled. |
9500 |
|
Path to the instance log4j config file. If set, appends the appropriate log appender automatically (including the port specified above). |
/var/lib/neo4j/conf/server-logs.xml |
|
Minimum duration in milliseconds for a query to be logged (optional) |
100 |
|
Enable filter for errors under the minimum duration in milliseconds (optional) |
true |
|
Disable the string literal obfuscation in queries (optional) |
true |
|
Collect and show queries coming from the NOM agent (optional) |
true |
|
Agents are supposed to monitor only local instances and should not be configured to connect to remote instances. |
|
Refer to Neo4j instance requirements to ensure that all instances meet the requirements to be managed by NOM. |