Clone nodes
The available procedures are described in the table below:
| Qualified Name | Type | Release |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Example Usage
The examples below will help us learn how to use these procedures.
Clone nodes only
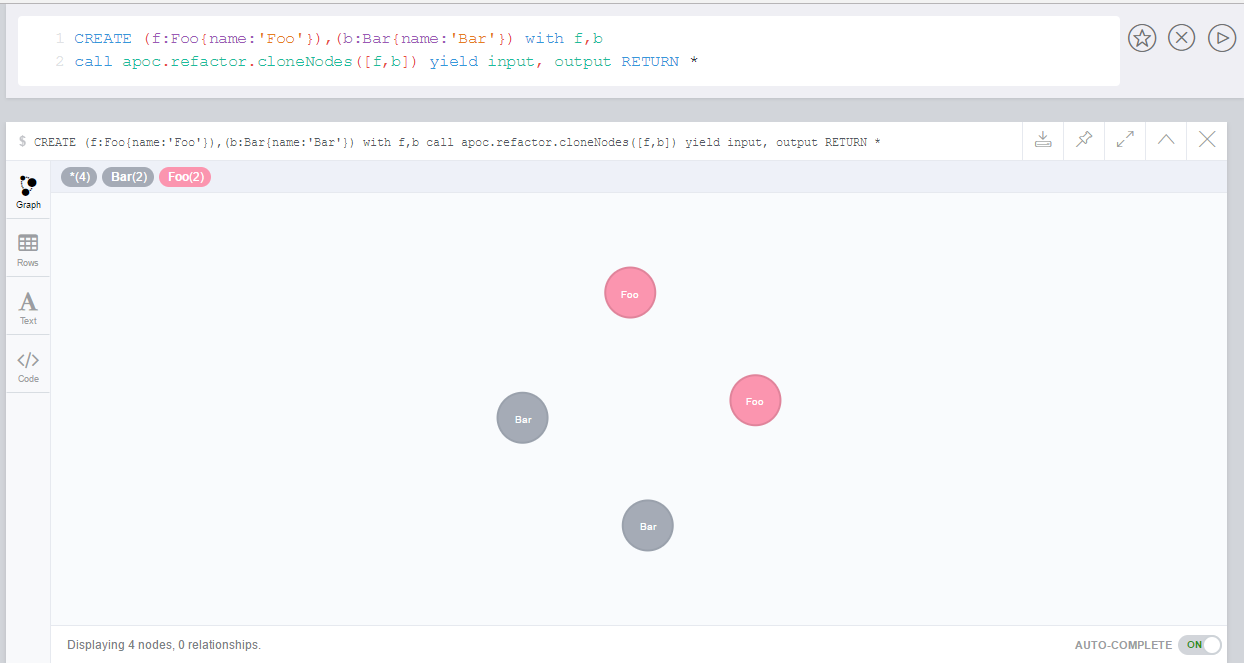
The following creates a graph with two nodes, Foo and Bar:
CREATE (f:Foo{name:'Foo'}),(b:Bar{name:'Bar'})
The following creates copies of both of these nodes:
MATCH (f:Foo{name:'Foo'}),(b:Bar{name:'Bar'})
CALL apoc.refactor.cloneNodes([f,b])
YIELD input, output
RETURN *If we execute this query, it will result in the following graph:
Clone nodes with relationships
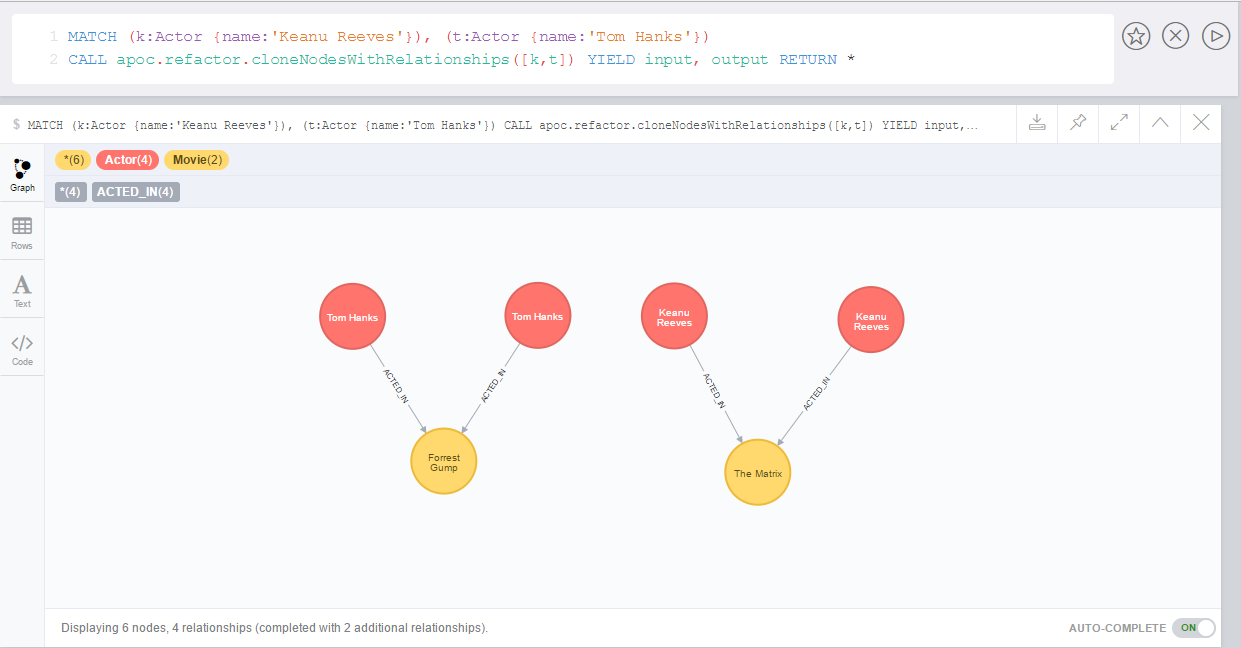
The following creates a graph containing two different nodes of type
Actor connected with other two different node of type MovieCREATE (k:Actor {name:'Keanu Reeves'})-[:ACTED_IN {role:'Neo'}]->(m:Movie {title:'The Matrix'}),
(t:Actor {name:'Tom Hanks'})-[:ACTED_IN {role:'Forrest'}]->(f:Movie {title:'Forrest Gump'})
RETURN *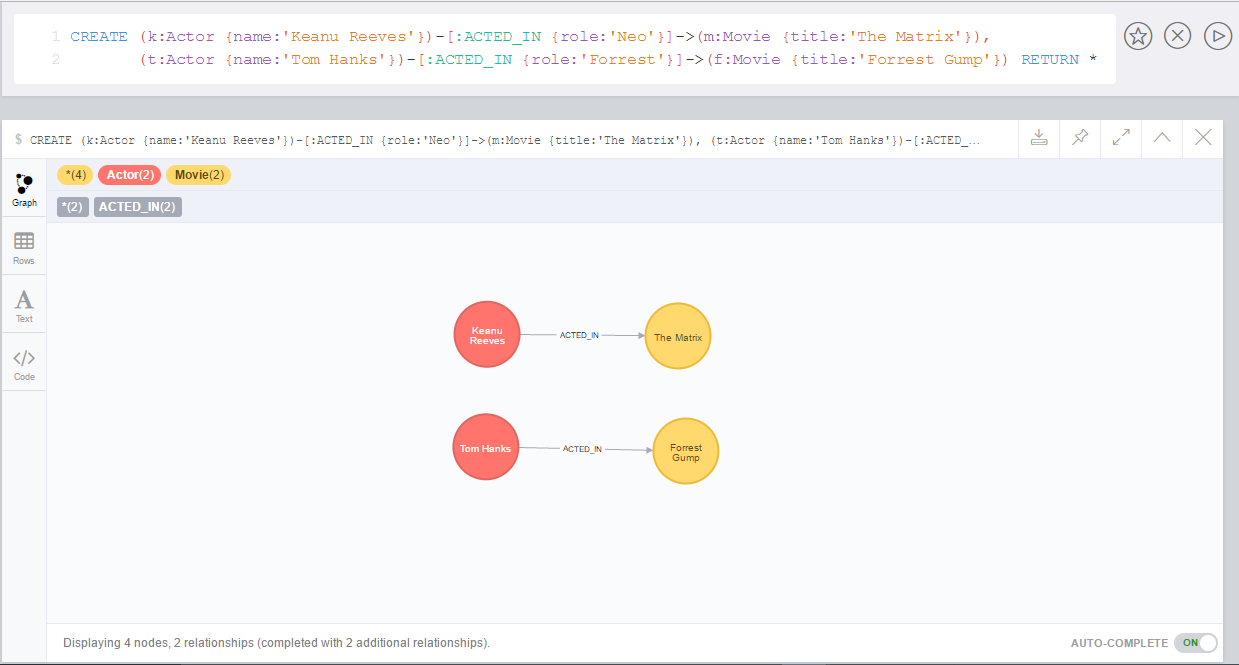
The following creates copies of both of these nodes and their relationships:
MATCH (k:Actor {name:'Keanu Reeves'}), (t:Actor {name:'Tom Hanks'})
CALL apoc.refactor.cloneNodesWithRelationships([k,t])
YIELD input, output
RETURN *As result we have a copy of the nodes and relationships