Memory Estimation
The graph algorithms library operates completely on the heap, which means we’ll need to configure our Neo4j Server with a much larger heap size than we would for transactional workloads. The diagram belows shows how memory is used by the projected graph model:
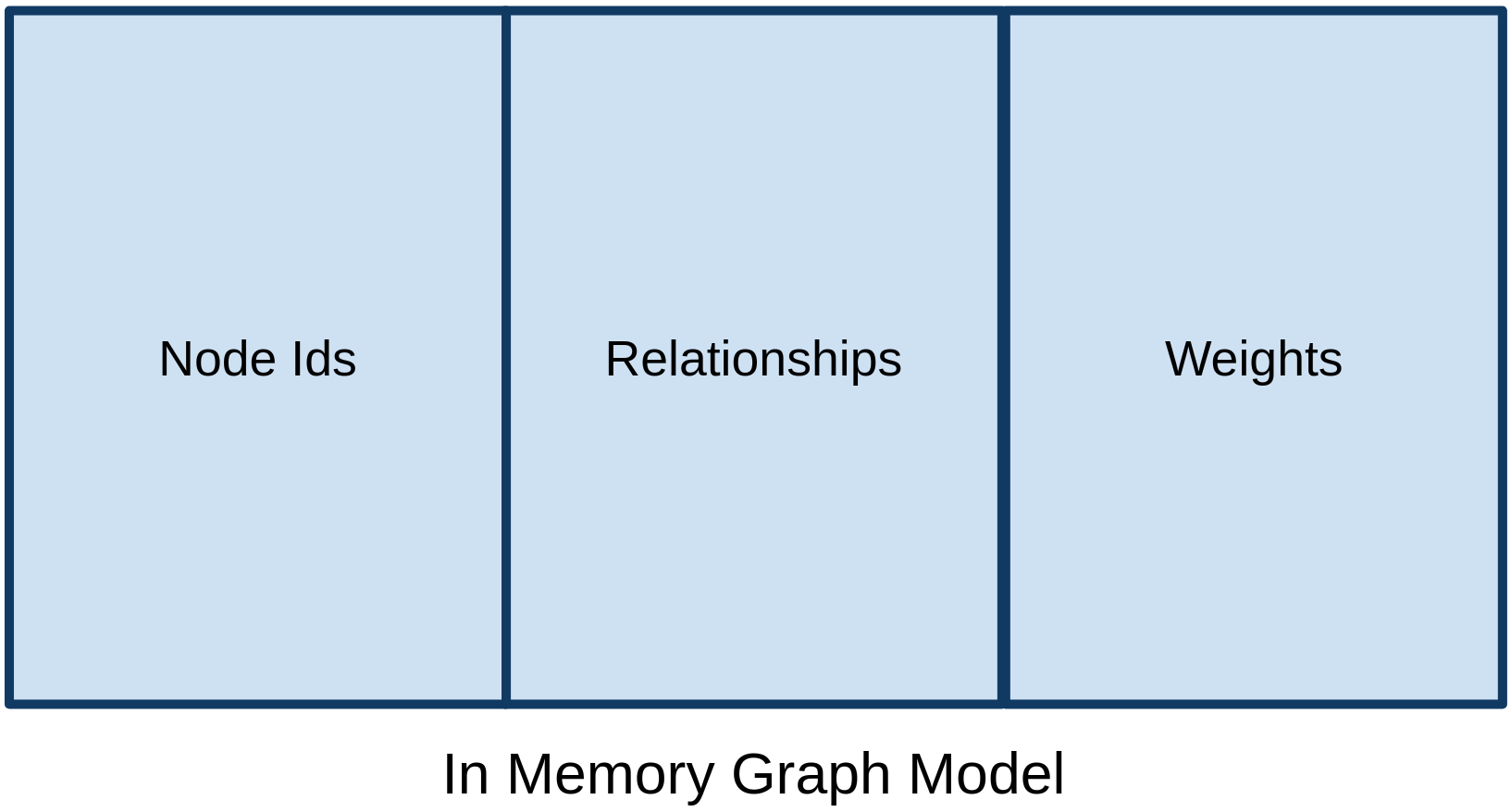
The model contains three types of data:
-
Node ids - up to 245 ("35 trillion")
-
Relationships - pairs of node ids. Relationships are stored twice if
orientation: "UNDIRECTED"is used. -
Weights - stored as doubles (8 bytes per node) in an array-like data structure next to the relationships
Memory configuration depends on the graph projection that we’re using.
Estimating memory requirements for algorithms
In many use cases it will be useful to estimate the required memory of projecting a graph and running an algorithm before running it in order to make sure that the workload can run on the available free memory.
To do this the .estimate mode can be used, which returns an estimate of the amount of memory required to run graph algorithms.
Note that only algorithms in the production-ready tier are guaranteed to have an .estimate mode.
For more details please refer to Syntax overview.
CALL gds[.<tier>].<algorithm>.<execution-mode>.estimate(
graphNameOrConfig: String or Map,
configuration: Map
) YIELD
nodeCount: Integer,
relationshipCount: Integer,
requiredMemory: String,
treeView: String,
mapView: Map,
bytesMin: Integer,
bytesMax: Integer,
heapPercentageMin: Float,
heapPercentageMax: Float| Name | Type | Default | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
graphNameOrConfig |
String or Map |
- |
no |
The name of the projected graph or a configuration to project a graph. |
configuration |
Map |
- |
no |
The configuration of the algorithm. |
The configuration map accepts the same configuration parameters as the estimated algorithm. See the specific algorithm documentation for more information.
In contrast to procedures that execute algorithms, for memory estimation it is possible to define a graph projection config. With this it is possible to measure the memory consumption of projecting a graph and executing the algorithm at the same time.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Integer |
The number of nodes in the graph. |
|
Integer |
The number of relationships in the graph. |
|
String |
An estimation of the required memory in a human readable format. |
|
String |
A more detailed representation of the required memory, including estimates of the different components in human readable format. |
|
Map |
A more detailed representation of the required memory, including estimates of the different components in structured format. |
|
Integer |
The minimum number of bytes required. |
|
Integer |
The maximum number of bytes required. |
|
Float |
The minimum percentage of the configured maximum heap required. |
|
Float |
The maximum percentage of the configured maximum heap required. |
Graph creation configuration
| Name | Type | Default | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
String, List of String or Map |
null |
yes |
The node projection used for anonymous graph creation via a Native projection. |
|
String, List of String or Map |
null |
yes |
The relationship projection used for anonymous graph creation a Native projection. |
|
nodeQuery |
String |
null |
yes |
The Cypher query used to select the nodes for anonymous graph creation via a Legacy Cypher projection. |
relationshipQuery |
String |
null |
yes |
The Cypher query used to select the relationships for anonymous graph creation via a Legacy Cypher projection. |
nodeProperties |
String, List of String or Map |
null |
yes |
The node properties to project during anonymous graph creation. |
relationshipProperties |
String, List of String or Map |
null |
yes |
The relationship properties to project during anonymous graph creation. |
Integer |
4 [1] |
yes |
The number of concurrent threads used for running the algorithm. |
|
String |
Generated internally |
yes |
An ID that can be provided to more easily track the algorithm’s progress. |
|
Boolean |
true |
yes |
If disabled the progress percentage will not be logged. |
|
readConcurrency |
Integer |
value of 'concurrency' |
yes |
The number of concurrent threads used for creating the graph. |
1. In a GDS Session the default is the number of available processors |
||||
Estimating memory requirements for graphs
The gds.graph.project procedures also support .estimate to estimate memory usage for just the graph.
Those procedures don’t accept the graph name as the first argument, as they don’t actually project the graph.
CALL gds.graph.project.estimate(nodeProjection: String|List|Map, relationshipProjection: String|List|Map, configuration: Map)
YIELD requiredMemory, treeView, mapView, bytesMin, bytesMax, heapPercentageMin, heapPercentageMax, nodeCount, relationshipCountThe nodeProjection and relationshipProjection parameters follow the same syntax as in gds.graph.project.
| Name | Type | Default | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
nodeProjection |
String or List or Map |
- |
no |
The node projection to estimate for. |
relationshipProjection |
String or List or Map |
- |
no |
The relationship projection to estimate for. |
configuration |
Map |
{} |
yes |
Additional configuration, such as concurrency. |
The result of running gds.graph.project.estimate has the same form as the algorithm memory estimation results above.
It is also possible to estimate the memory of a fictive graph, by explicitly specifying its node and relationship count. Using this feature, one can estimate the memory consumption of an arbitrarily sized graph.
To achieve this, use the following configuration options:
| Name | Type | Default | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
nodeCount |
Integer |
0 |
yes |
The number of nodes in a fictive graph. |
relationshipCount |
Integer |
0 |
yes |
The number of relationships in a fictive graph. |
When estimating a fictive graph, syntactically valid nodeProjection and relationshipProjection must be specified.
However, it is recommended to specify '*' for both in the fictive graph case as this does not interfere with the specified values above.
The query below is an example of estimating a fictive graph with 100 nodes and 1000 relationships.
CALL gds.graph.project.estimate('*', '*', {
nodeCount: 100,
relationshipCount: 1000,
nodeProperties: 'foo',
relationshipProperties: 'bar'
})
YIELD requiredMemory, treeView, mapView, bytesMin, bytesMax, nodeCount, relationshipCount| requiredMemory | bytesMin | bytesMax | nodeCount | relationshipCount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"593 KiB" |
607576 |
607576 |
100 |
1000 |
The gds.graph.project.cypher procedure has to execute both, the nodeQuery and relationshipQuery, in order to count the number of nodes and relationships of the graph.
CALL gds.graph.project.cypher.estimate(nodeQuery: String, relationshipQuery: String, configuration: Map)
YIELD requiredMemory, treeView, mapView, bytesMin, bytesMax, heapPercentageMin, heapPercentageMax, nodeCount, relationshipCount| Name | Type | Default | Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
nodeQuery |
String |
- |
no |
The node query to estimate for. |
relationshipQuery |
String |
- |
no |
The relationship query to estimate for. |
configuration |
Map |
{} |
yes |
Additional configuration, such as concurrency. |
Automatic estimation and execution blocking
All procedures in the GDS library that support estimation, including graph creation, will do an estimation check at the beginning of their execution.
This includes all execution modes, but not the estimate procedures themselves.
If the estimation check can determine that the current amount of free memory is insufficient to carry through the operation, the operation will be aborted and an error will be reported. The error will contain details of the estimation and the free memory at the time of estimation.
This heap control logic is restrictive in the sense that it only blocks executions that are certain to not fit into memory. It does not guarantee that an execution that passed the heap control will succeed without depleting memory. Thus, it is still useful to first run the estimation mode before running an algorithm or graph creation on a large data set, in order to view all details of the estimation.
The free memory taken into consideration is based on the Java runtime system information. The amount of free memory can be increased by either dropping unused graphs from the catalog, or by increasing the maximum heap size prior to starting the Neo4j instance.
Bypassing heap control
Occasionally you will want the ability to bypass heap control if it is too restrictive. You might have insights into how your particular procedure call will behave, memory-wise; or you might just want to take a chance e.g. because the memory estimate you received is very close to system limits.
For that use case we have sudo mode which allows you to manually skip heap control and run your procedure regardless. Sudo mode is off by default to protect users - we fail fast if we can see your potentially long-running procedure would not be able to complete successfully.
To enable sudo mode, add the sudo parameter when calling a procedure. Here is an example of calling the popular Louvain community detection algorithm in sudo mode:
CALL gds.louvain.write('myGraph', { writeProperty: 'community', sudo: true })
YIELD communityCount, modularity, modularitiesAccidentally enabling sudo mode when calling a procedure, causing it to run out of memory, will not significantly damage your installation, but it will waste your time.